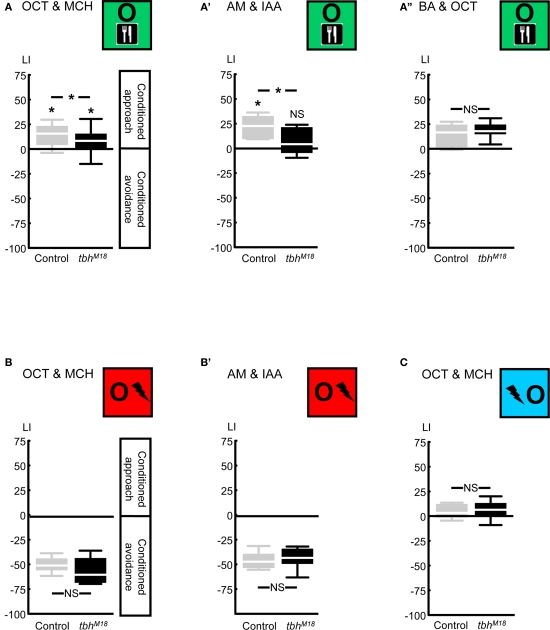
Figure 6.
Compromising octopamine biosynthesis using the Tβ H mutant. We used the tbhM18 mutant, which has reduced or no octopamine. When the odors 3-octanol (OCT) and 4-methylcyclohexanol (MCH) were used, reward learning was partially impaired (A). Using the odors n-amyl acetate (AM) and isoamyl acetate (IAA) revealed complete lack of reward learning in the tbhM18 mutant (A′). When the odors OCT and benzaldehyde (BA) were used, tbhM18 mutant was intact in reward learning (A′′). A modified punishment learning procedure, which was identical to reward learning, except that the shock pulses were replaced by sugar presentation, revealed no impairment in the tbhM18 mutant, when either the odors OCT and MCH (B) or AM and IAA (B′) were used. Finally, under those conditions for which reward learning of the tbhM18 mutant was partially impaired, i.e., using the odors OCT and MCH, relief learning remained unaffected (C). For this experiment, the odors AM and IAA were not used, as these do not support relief learning (Yarali et al., 2008, loc. cit. Figure 5D). *P < 0.05, NS: P > 0.05, while comparing between genotypes. While comparing scores of each genotype to 0 *P < 0.05/2, NS: P > 0.05/2 (i.e., Bonferroni correction). Sample sizes were from left to right N = 40, 39 in (A), 11, 13 in (A′), 23, 22 in (A′′), 12, 12 in (B), 9, 9 in (B′), and 20, 20 in (C). Box plots are as detailed in Figure 4.