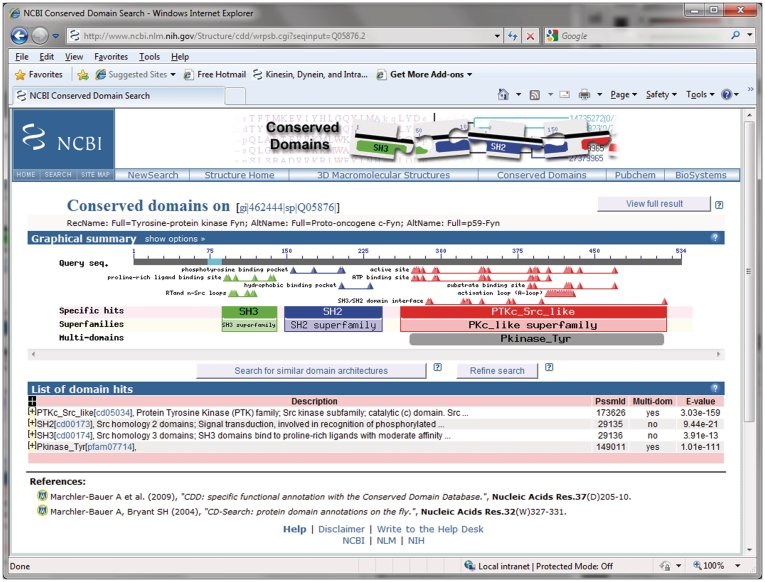
Figure 1.
Conserved domain annotation on a well-characterized protein sequence. Shown here is the default concise view generated by the CD-Search tool, using pre-calculated alignment information. The view is divided into two panels: a graphical summary and a table detailing the individual matches. The query sequence coordinates are indicated on a gray bar in the top portion of the graphical summary. ‘Specific hits’ to NCBI-curated domain models are positioned in a separate area below the query sequence, with corresponding balloons rendered in saturated colors. The extent of the best-scoring hit for a region on the query also determines the annotation with the corresponding conserved domain ‘Superfamily’. ‘Superfamilies’ are positioned in the area below the ‘Specific hits’, and together these are enclosed in boxes to indicate superfamily membership of the NCBI-curated models. If the full (detailed) results display is selected, an area summarizing ‘Non-specific hits’ will be shown as well, and the corresponding boxes will be drawn so as to resolve their superfamily relationships; the highest ranked match for each superfamily defines the extents of the corresponding box. ‘Non-specific hits’ and ‘Superfamily’ balloons are rendered in pastel colors, with each superfamily being assigned a separate color. Matches to ‘multi-domain’ models are rendered as gray balloons in a separate area of the summary graph. Only the best-ranked non-overlapping multi-domain models are shown. Functional sites, as annotated on NCBI-curated domain models, are mapped to the query sequence and depicted as triangles. Sites are mapped from the highest ranked model only, and they are colored according to their source. Both conserved domain balloons and site annotations are hot-linked, so that moving the mouse over the objects displays additional information, and so that clicking on the objects launches conserved domain summary pages for the particular domain model, embedding the user query sequence in the alignment for further analysis, if applicable. A tabular view below the graphical summary lists E-values, multi-domain status and various identifiers for the conserved domain models identified as matches. The table rows can be expanded to display a detailed pair-wise sequence alignment between the query sequence and the domain model’s consensus sequence. An alignment of all sequences comprising a domain model, with or without the query sequence embedded, is accessible by clicking on the domain’s balloon representation in the graphical summary or its unique accession in the tabular summary, respectively.