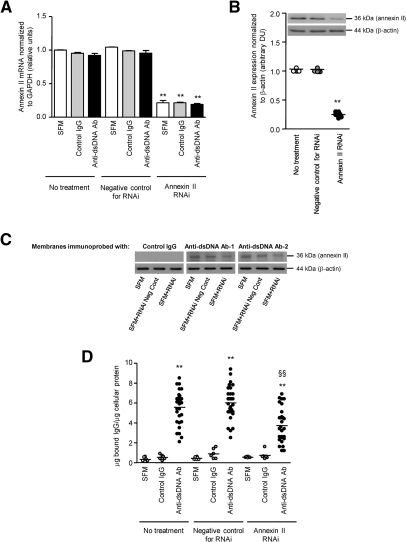
Figure 11.
Suppression of annexin II expression in HMC by RNAi reduces anti-dsDNA binding. (A) Annexin II transcript in HMC incubated with SFM, control IgG, or seven different anti-dsDNA antibodies with or without prior RNAi treatment. **P < 0.001 for RNAi versus RNAi negative control or no treatment for the same stimulus. (B) Annexin II protein expression in HMC incubated with SFM (no treatment) with or without prior RNAi treatment. A representative Western blot is shown. The ECL signal was semiquantified by gel documentation, normalized to β-actin, and expressed as arbitrary densitometric units. **P < 0.001 for RNAi versus RNAi negative control or no treatment. (C) Cell lysates were extracted from transfected and nontransfected HMC, subjected to Western blot, and probed with control IgG and two different human anti-dsDNA antibodies. Annexin II suppression with RNAi resulted in decreased binding by anti-dsDNA antibodies compared with samples isolated from untreated (SFM) cells or those transfected with RNAi negative control. The samples were normalized to β-actin. (D) Binding of anti-dsDNA antibodies to HMC, with or without prior RNAi treatment, was assessed by cellular ELISA and expressed as μg of bound IgG/μg of cellular protein.21 The horizontal line in each group represents the mean level. **P < 0.001 for anti-dsDNA Ab versus SFM or control IgG for same treatment; §§P < 0.001 for anti-dsDNA Ab or anti-dsDNA Ab + RNAi negative control versus anti-DNA Ab + RNAi.