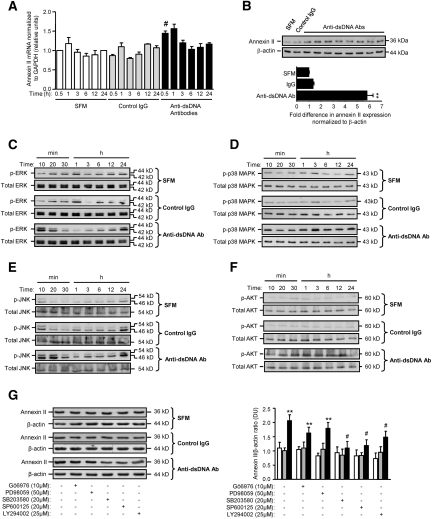
Figure 9.
Anti-dsDNA antibodies induce annexin II and ERK, p38 MAPK, JNK, and AKT activation in HMC. (A) Annexin II transcript in HMC incubated with SFM, control IgG, or six different human polyclonal anti-dsDNA antibodies as determined by real-time PCR. #P < 0.05 for anti-dsDNA Ab versus SFM or control IgG after 30 minutes of incubation. (B) Western blot showing the effect of SFM, control human IgG, or eight different human polyclonal anti-dsDNA antibody preparations on annexin II expression in total mesangial cell lysate (upper panel). The ECL signal was semiquantified by gel documentation, normalized to β-actin, and expressed as the mean ± SD fold difference (lower panel) compared with SFM or control IgG. **P < 0.001 for anti-dsDNA Ab versus SFM or control IgG. (C through F) Representative Western blots showing the effect of SFM, control IgG, and anti-dsDNA antibodies on ERK activation (p-ERK) (C), p38 MAPK activation (p-p38 MAPK) (D), JNK activation (p-JNK) (E), and AKT activation (p-AKT) (F). (G) Representative Western blot (left panel) showing the effects of specific inhibitors to PKC, ERK, p38 MAPK, JNK, and PI3K on annexin II synthesis in HMC incubated with SFM (white bars), control IgG (gray bars), and anti-dsDNA antibodies (black bars). The ECL signal was semiquantified by gel documentation, normalized to β-actin, and expressed as the mean ± SD fold difference compared with SFM (right panel). **P < 0.001 for anti-dsDNA Ab versus SFM or control IgG for the same treatment; #P < 0.05, with versus without inhibitor.