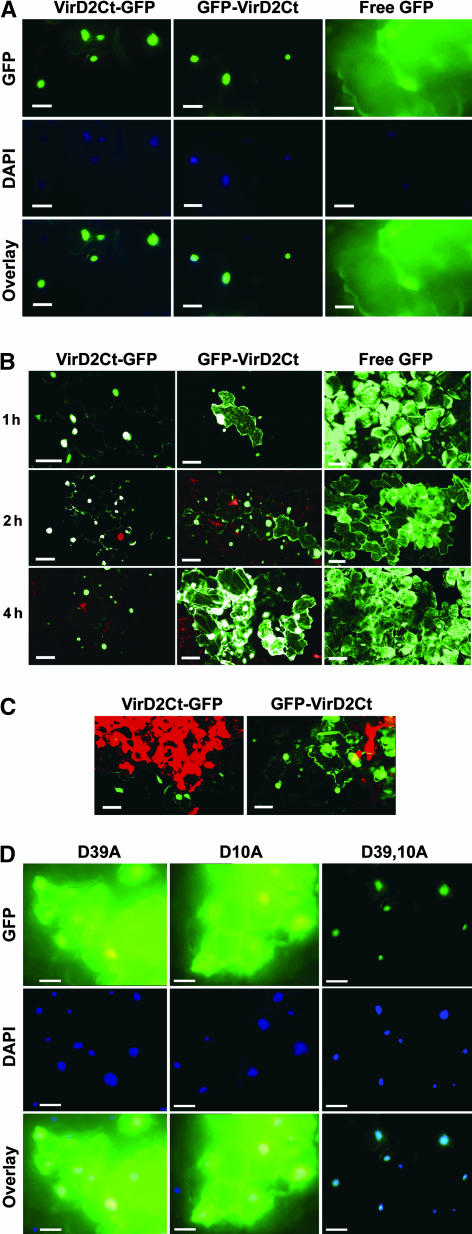
Figure 3.
Intracellular Localization of VirD2Ct Derivatives Expressed as Fusions with GFP from a TMV(30B) Vector in Tobacco Samsun NN Plants during the HR.
(A) Fluorescence micrographs showing the nuclear localization of VirD2Ct-GFP and GFP-VirD2Ct in Samsun NN cells at 33°C (in the absence of HR). Free GFP expressed from a TMV(30B) vector was used as a control. 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining was used to visualize nuclei. The overlay images represent a superimposition of blue and green signals. Bars = 50 μm.
(B) Confocal images showing the intracellular localization of VirD2Ct-GFP and GFP-VirD2Ct in Samsun NN plants transferred from 33 to 24°C at 1, 2, and 4 h after transfer. Free GFP expressed from a TMV(30B) vector was used as a control. Bars = 50 μm.
(C) Confocal images showing the intracellular localization of VirD2Ct-GFP and GFP-VirD2Ct in Samsun NN at 24°C in a group of infected cells located at different distances from the center of a necrotic lesion (red). Bars = 50 μm.
(D) Fluorescence micrographs showing the intracellular localization of GFP-VirD2Ct containing single D10A and D39A and double D10,39A mutations in Samsun NN plants transferred from 33 to 24°C at 4 h after transfer. DAPI staining was used to visualize nuclei. The overlay images represent a superimposition of blue and green signals. Bars = 50 μm.