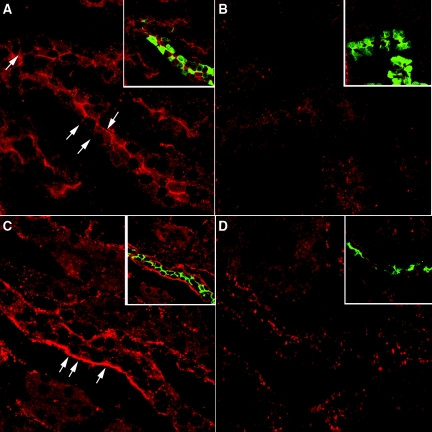
Figure 7.
Indirect immunofluorescence images of kidney showing CT receptor in cortical collecting ducts and connecting segments. One rat kidney was fixed by immersion, sectioned and immunostained to detect the CT receptor as well as AQP2 and calbindin. The CT receptor is located in the apical membrane in cortical tubules (A) that costain for calbindin (A, inset, green), a marker of cortical connecting segments. Apical staining is completely abolished in the presence of directed antibody peptide (B) in calbindin-positive tubules (B, inset). Mainly basolateral CT receptor staining was observed in cortical collecting ducts (C). Both the CT receptor (red) and AQP2 (green) colocalized in the same cells (C, inset). This CT receptor staining was abolished in the presence of peptide inhibitor (D, inset), although some spots of nonspecific fluorescence remain scattered throughout the section. The images are representative of three independent experiments.