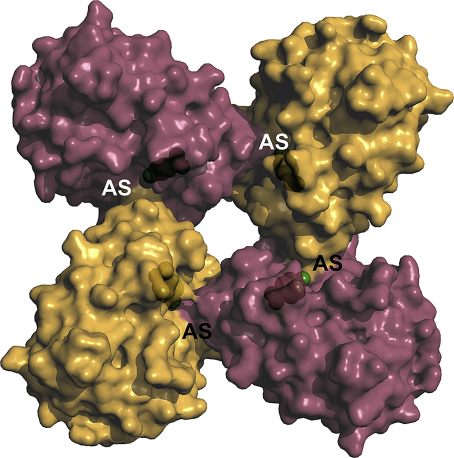
Fig. 6.
Potential autoinhibitory homocomplex of KLK4 with monomers depicted as alternating purple and orange surface representations. In solution and in crystals KLK4 forms oligomers, consisting of cyclic tetramers that assemble to octamers, or even higher oligomers, such as dimers and tetramers of octamers. Due to intermolecular contacts, the active site clefts of KLK4 become very narrow at the catalytic centers (labelled AS) with Ser195 shown as green balls. In particular the S1 and S2 subsites are hardly accessible for small chromogenic and fluorogenic substrates, not to mention large protein substrates [137].