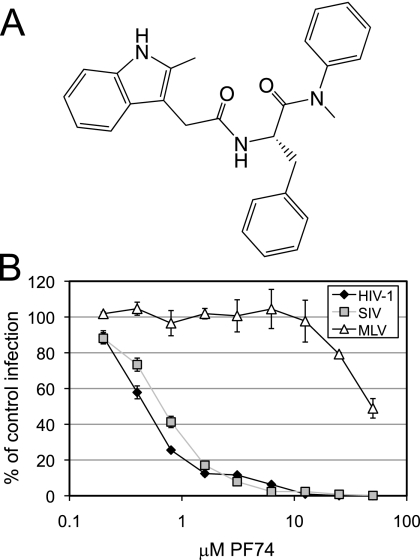
FIG. 1.
PF74 selectively inhibits infection by HIV-1. (A) Chemical structure of PF74. (B) Selectivity of PF74 antiviral activity. VSV-G-pseudotyped HIV-1, SIV, and lacZ-transducing MLV vector particles were inoculated on HeLa-P4 indicator cells in the presence of the indicated concentrations of PF74. In the case of HIV-1 and SIV, expression of viral Tat protein in the target cells transactivates an LTR-lacZ reporter, resulting in the expression of β-galactosidase. For the MLV vector particles, transduction of the lacZ-containing vector results in expression of β-galactosidase. Two days after inoculation, the cultures were fixed and stained with X-Gal, and blue cells were enumerated by digital image processing. Shown is the percentage of infection at the corresponding inhibitor concentrations, with error bars representing the standard deviations of the means of the triplicate determinations. The results are representative of four independent experiments.