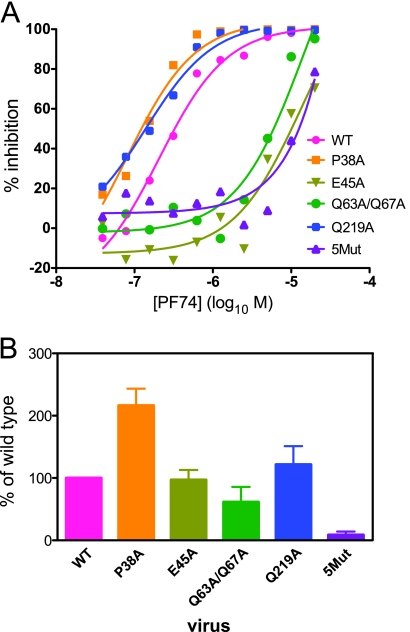
FIG. 4.
Mutations that alter HIV-1 core stability modulate HIV-1 sensitivity to PF74. (A) Wild-type and mutant HIV-1 viruses were titrated on HeLa-P4 cells in the presence of various concentrations of PF74. For each virus, infection at each concentration of PF74 was calculated as a percentage of the corresponding untreated virus infection. The experiment was performed more than three times, with similar results. (B) Binding of 3H-PF74 to the indicated HIV-1 mutant particles was tested. Samples of concentrated virus particles were incubated with the radiolabeled compound, pelleted, resuspended in PBS, and then repelleted through a 20% sucrose cushion. The pelleted particles were dissolved in sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing sample buffer, and the levels of 3H and CA protein were quantified by liquid scintillation counting and ELISA, respectively. The ratios of the radioactive signals to the CA protein were calculated and expressed as a percentage of the wild-type value. Shown are the mean values obtained from averaging the data from at least six independent experiments, with error bars representing one standard deviation.