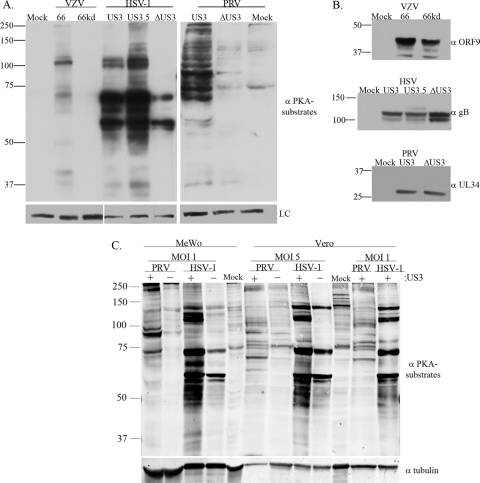
FIG. 1.
Anti-PKAps profiles for cells infected with alphaherpesviruses (VZV, HSV-1, or PRV) with or without expression of their US3 kinases. MeWo cells were either mock infected, infected at an MOI of 0.1 with VZV.GFP-66 or VZV.GFP-66kd (expressing kinase-inactivated ORF66 protein), or infected at an MOI of 1 with HSV-1 (US3), HSV-EGFP-US3.5 (US3.5), HSV-EGFP-ΔUS3 (ΔUS3), PRV (US3), or PRV.ΔUS3 (ΔUS3). Cell extracts were harvested 20 h postinfection and were separated on a 7% SDS-PAGE gel. (A) Immunoblot analysis of proteins is shown following antibody probing with a rabbit α-p-PKA substrate antibody (top) or a mouse α-tubulin (VZV and PRV) or α-Ku-86 (HSV-1) antibody (bottom) as a loading control (LC). (B) Immunoblot analysis of viral proteins to show equal infections (rabbit α-VZV ORF9, mouse α-HSV gB, or goat α-PRV UL34 antibody). (C) Comparisons of the anti-PKAps profiles of MeWo cells or Vero cells infected with HSV-1 or PRV, either with (+) or deleted for (−) the US3 kinase. Profiles of cells infected at two different multiplicities of infection (1 and 5) for each virus, harvested at 18 h postinfection, are shown. The same blot was simultaneously probed with antibodies to tubulin for a loading control. Antibodies in panels A and B were detected by use of secondary antibodies bound to horseradish peroxidase, followed by a fluorescent substrate and collection by film exposure. Antibodies in panel C were simultaneously detected using secondary antibodies linked to IRDye 800CW (anti-mouse) or IRDye 680 (anti-rabbit) and were captured by a LI-COR Odyssey infrared imager. Protein size markers (in kilodaltons) are specified to the left of each panel.