FIG. 3.
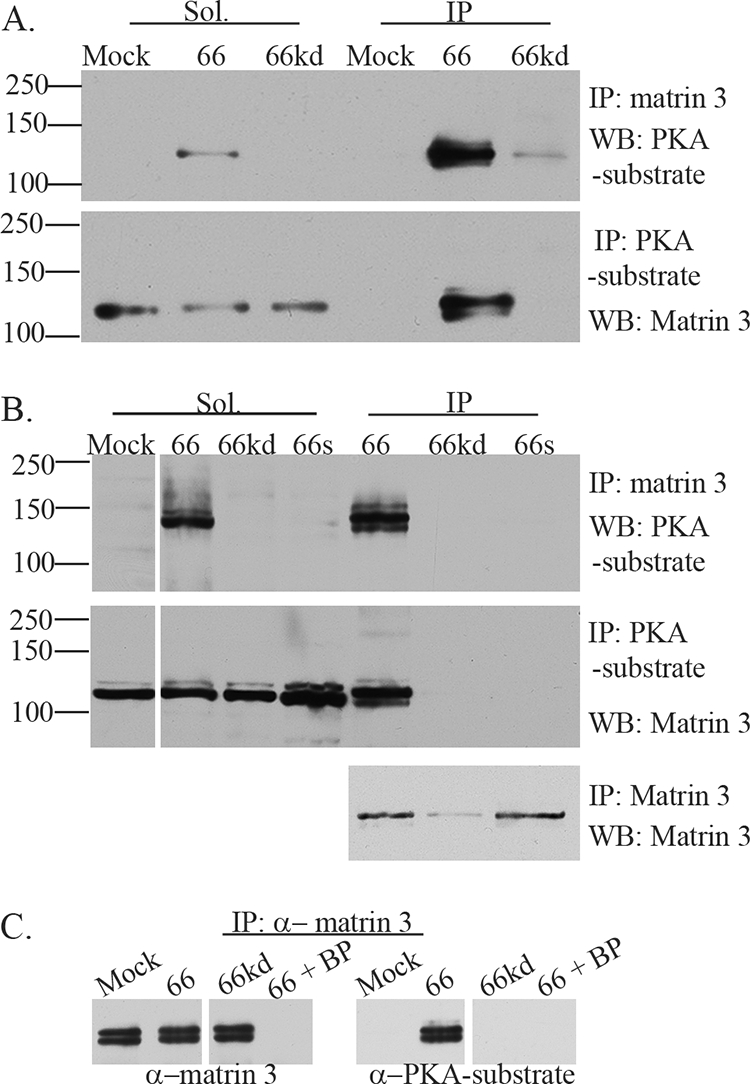
VZV ORF66 kinase activity induces specific matrin 3 phosphorylation. (A) Hek 293 cells were either infected with Ad.GFP-66 or Ad.GFP-66kd at an MOI of 0.3 or mock infected and were then incubated for 24 h. Soluble fractions (Sol) and immunoprecipitation (IP) products were separated on a 7% gel and analyzed by immunoblotting (Western blotting [WB]). IPs were performed using rabbit α-matrin 3, followed by probing of membranes with the rabbit α-PKA substrate antibody (top), or IPs were performed using the rabbit α-PKA substrate antibody, followed by probing of membranes with the rabbit α-matrin 3 antibody (bottom). (B) MRC-5 cells either were infected with VZV.GFP-66 (66), VZV.GFP-66kd (66kd), or VZV.GFP-66s (66s) at an MOI of 0.01 or were mock infected; then they were harvested 2 days postinfection. Soluble extracts (Sol) or immunoprecipitations were separated on a 7% SDS-PAGE gel and were immunoblotted (top and center) as described above. The top membrane was then stripped and reprobed for matrin 3 to analyze levels of matrin 3 in IP fractions (bottom). Protein size markers (in kilodaltons) are specified to the left. (C) MRC-5 cells either were infected with VZV expressing ORF66 or ORF66kd at an MOI of 0.01 or were mock infected; they were harvested at 2 days postinfection. Cleared lysates were then immunoprecipitated using a rabbit α-matrin 3 antibody in addition to matrin 3 blocking peptide (BP) where indicated. Proteins were separated on a 6% SDS-PAGE gel, and membranes were then probed either with a rabbit α-matrin 3 antibody (left), to test for the efficiency of IPs and the blocking peptide, or with a rabbit α-PKA substrate antibody, to analyze for phosphorylation of matrin 3 (right).
