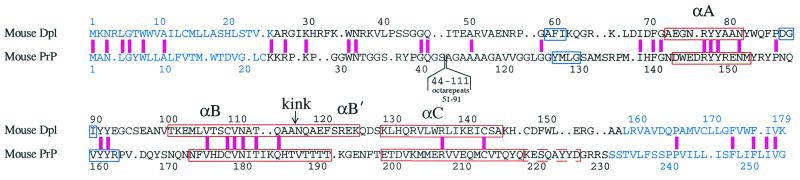
Figure 1.
Alignment of the amino acid sequences of mouse Dpl (19) and mouse PrPC (46). The sequences of the 26–157 construct of Dpl used in the present work, and of the 23–231 construct of mouse PrPC (47), are shown in black letters. Blue letters compose the signal sequence at the N terminus and the C-terminal hydrophobic region. The octarepeat sequence of PrPC (not present in Dpl) has been omitted for brevity. The pink bar indicates identical amino acids. Red and blue boxes indicate the location of α and β secondary structures in Dpl (this work) and mouse PrPC (3). Helices are labeled αA, αB, and αC; the location of the kink in the αB helix is shown. αB′ indicates the B helix C-terminal to the kink. The dashed red box at residues 220–227 of PrPC shows the location of the extended αC helix in Syrian hamster (4), bovine (5), and human (6) PrPC.