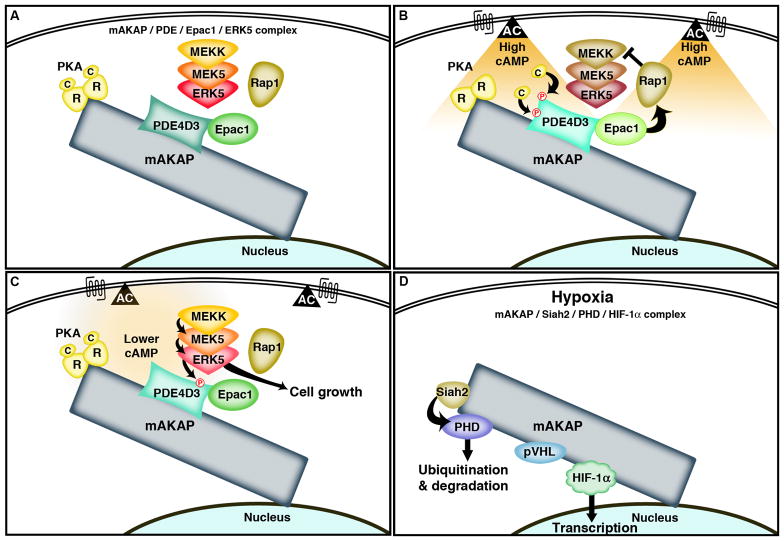
Fig. 1. mAKAP signaling complexes.
A) mAKAP assembles a cAMP-responsive complex of signaling enzymes at the perinuclear membrane in the heart. PKA, PDE4D3 Epac1 and ERK5 are brought together with other associated enzymes to control different aspects of cardiomyocyte physiology. B) When intracellular cAMP levels are elevated the mAKAP-associated PKA phosphorylates the PDE4D3 in the complex at two sites, leading to increased metabolism of cAMP by the phosphodiesterase. Likewise, cAMP activation of Epac1 in the complex activates Rap1 to inhibit ERK5 signaling. C) As cAMP levels fall, the Epac1-mediated inhibition of ERK signaling is lost and mitogenic signaling favors cell growth. D) mAKAP assembles an oxygen sensitive signaling pathway that includes the ubiquitin E3 ligase Siah2, prolyl hydroxylase, von Hippel-Lindau protein and the transcription factor HIF-1α. Under normoxic conditions, HIF-1α is continually degraded however, when oxygen levels fall, the mAKAP associated PHD is degraded and HIF-1α accumulates and translocates into the nucleus.