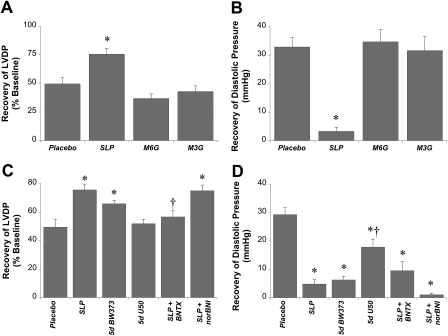
Fig. 4.
Relative roles of opioid receptor subtypes in triggering SLP. Effects of opioid receptor antagonists or agonists were assessed. A and B, data are shown for the effects on recoveries for LVDP (percentage of baseline) (A) and end-diastolic pressure (mmHg) (B) after 5-day exposure to placebo, morphine, morphine-6-glucuronide (M6G), or morphine-3-glucuronide (M3G). C and D, data are shown for recoveries for LVDP (percentage of baseline) (C) and end-diastolic pressure(mmHg) (D), where mice were subjected to 5-day (5d) morphine-induced SLP in the absence or presence of a δ-selective antagonist (BNTX) or κ-opioid antagonist (nor-BNI). We also assessed effects of 5-day exposure to a δ-opioid-selective agonist (BW373U86) or the κ-selective agonist U50,488H (U50). Hearts were isolated for ex vivo assessment of functional sensitivity to 25-min ischemia/45-min reperfusion. Data are means ± S.E.M. *, P < 0.05 versus placebo; †, P < 0.05 versus SLP alone.