Figure 1.
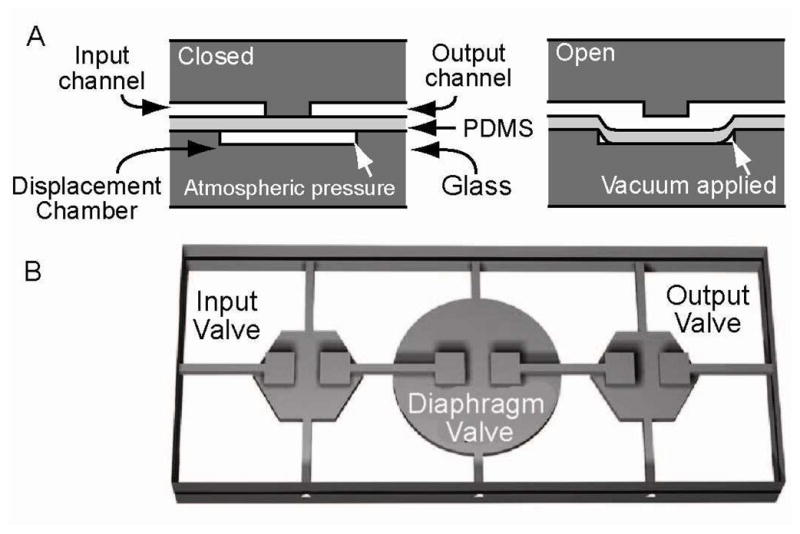
Cross sectional view through a monolithic membrane valve. The microvalves are composed of a featureless PDMS membrane sandwiched between a discontinuous fluidic channel and a pneumatic displacement chamber. (A) The valves are normally closed with the PDMS membrane resting on the valve seat. Application of a vacuum to the displacement chamber through a control channel pulls the PDMS membrane away from the discontinuity, allowing fluid to fill the chamber and/or flow across the discontinuity in the fluid channel. (B) Three independently actuated microvalves in series form an integrated micropump for transport of samples and reagents.
