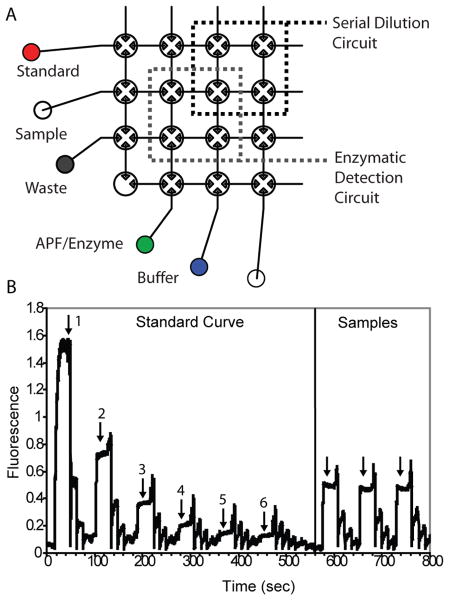
Figure 5.
(A) Details of a fully-automated assay for H2O2, a biomarker for oxidative stress. A H2O2 standard is diluted with buffer in the serial dilution circuit. A portion of the dilution is stored, and the remainder is transferred to the enzymatic detection circuit where it is mixed with aminophenyl fluorescein and horseradish peroxidase. During this phase, the aminophenyl fluorescein is oxidized to form a highly fluorescent product. After rinsing the enzymatic detection circuit, the stored H2O2 dilution is further diluted and the program is repeated to generate a standard curve. Finally, 120 nL samples are loaded and mixed with detection reagents for quantification. (B) Confocal fluorescence data acquired from the detection circuit during the performance of the assay. Arrows indicate the points in the assay where mixing is complete and data are collected.