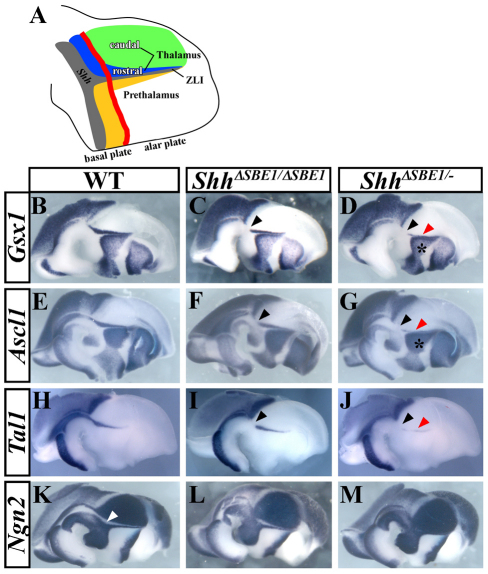
Fig. 4.
Rostral thalamic progenitor identity is dependent on Shh signaling from the ventral midline. (A) Schematic representation of a sagittal view through the mouse diencephalon, color coded as follows: gray, Shh-expressing cells; green, pTH-C domain; blue, pTH-R domain; yellow, prethalamic region; red line, border between the basal and alar plates. (B-M) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of genes expressed in pTH-R (Gsx1, Ascl1 and Tal1) and pTH-C (Ngn2) of wild-type (WT) and SBE1 mutant embryos at E12.5. The expression of genes in the pTH-R domain is missing (black arrowheads) or reduced (red arrowheads) to varying degrees in ShhΔSBE1/ΔSBE1 (C,F,I), and ShhΔSBE1/– (D,G,J) mutants. The prethalamic expression of Gsx1 and Ascl1 is not affected by the loss of SBE1 (asterisk in D,G). The gap in Ngn2 expression between pTH-C and the zli, corresponding to pTH-R (white arrowhead in K), is reduced in ShhΔSBE1/ΔSBE1 embryos (L) and absent in ShhΔSBE1/– embryos (M). pTH-C, caudal thalamic progenitors; pTH-R, rostral thalamic progenitors.