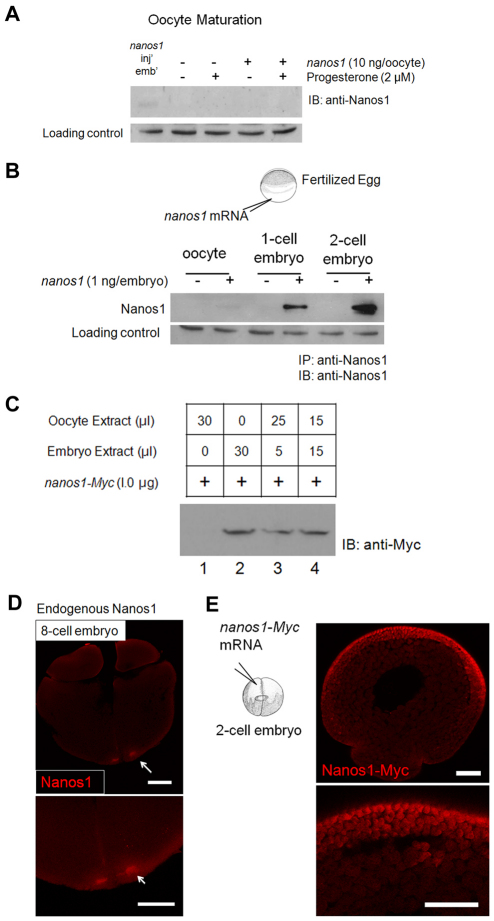
Fig. 5.
nanos1 repression is relieved only after fertilization. (A) nanos1 remains repressed during oocyte maturation events. Xenopus oocytes were injected with 10 ng of nanos1 transcript per oocyte and incubated at 18°C. To trigger maturation events, oocytes were incubated with progesterone (2 μM) and collected until at least 50% displayed germinal vesicle breakdown. Samples were analyzed by blotting with anti-Nanos1 antibody. nanos1-injected embryos served as a positive control. (B) Injected nanos1 transcripts are efficiently translated in embryos before first cleavage. One nanogram of capped transcript was injected into 1-cell stage embryos soon after fertilization. Embryos were collected at the indicated stages and protein extracts analyzed by blotting after immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-Nanos1 antibody. (C) nanos1-Myc was translationally active in the presence of embryo extract in a dose-independent fashion. One microgram of capped transcript was translated in vitro with oocyte and/or embryo extract. Samples were analyzed by blotting with anti-Myc antibody. (D) Endogenous Nanos1 was easily detected in the germ plasm by the 8-cell stage. Confocal immunofluorescence with anti-Nanos1 antibody. (E) Confocal immunofluorescence of embryos previously injected with nanos1-Myc RNA shows Nanos1 accumulation in somatic cells. Scale bars: 200 μm.