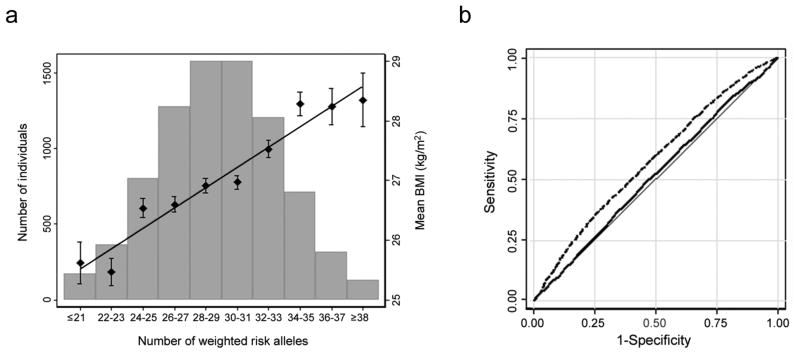
Figure 2. Combined impact of risk alleles on BMI/obesity.
(a) Combined effect of risk alleles on average BMI in the population-based Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study (n = 8,120 individuals of European descent). For each individual, the number of “best guess” replicated (n = 32) risk alleles from imputed data (0,1,2) per SNP was weighted for their relative effect sizes estimated from the stage 2 data. Weighted risk alleles were summed for each individual and the overall individual sum was rounded to the nearest integer to represent the individual’s risk allele score (range 16–44). Along the x-axis, individuals in each risk allele category are shown (grouped ≤21 and ≥38 at the extremes), and the mean BMI (+/− SEM) is plotted (y axis on right), with the line representing the regression of the mean BMI values across the risk-allele scores. The histogram (y-axis on left) represents the number of individuals in each risk-score category. (b) The area under the ROC curve (AUC) of two different models predicting the risk of obesity (BMI = ≥30 kg/m2) in the n = 8,120 genotyped individuals of European descent in the ARIC Study. Model 1, represented by the solid line, includes age, age2, and sex (AUC = 0.515, P = 0.023 for difference from AUCnull = 0.50). Model 2, represented by the dashed line, includes age, age2, sex, and the n = 32 confirmed BMI SNPs (AUC = 0.0575, P < 10−5 for difference from AUCnull = 0.50). The difference between both AUCs is significant (P < 10−4).