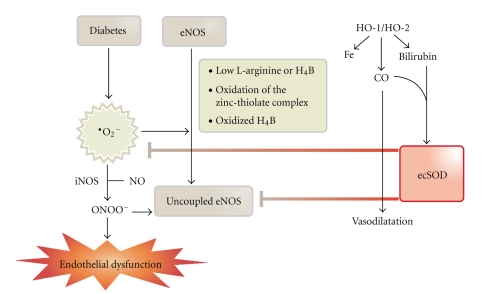
Figure 1.
The scheme summarizes the simplified mechanisms underlying oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction (and probably nitrate resistance) in diabetes mellitus. It should be noted that the oxidative stress concept provides an explanation for a part of diabetic complications and probably represents one important pathological pathway among several. Prevention of diabetic cardiovascular complications by induction of the heme oxygenase antioxidant system. Key mediators of these beneficial effects are carbon monoxide (CO) bilirubin, extracellular superoxide dismutase (ecSOD), coupling of endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) by normalization of tetrahydrobiopterin (H4B) levels, and decrease in superoxide levels. Adopted from Abraham and Kappas, Pharmacol. Rev. 2008 [31].