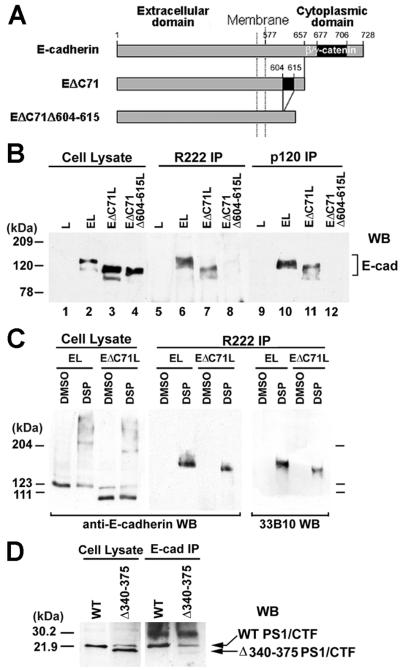
Figure 2.
PS1 binds E-cadherin independently of β- or γ-catenin. Cytoplasmic residues 604–615 are required for PS1/E-cadherin binding. (A) Schematic representation of mouse E-cadherin and E-cadherin deletion constructs EΔC71 and EΔC71Δ604–615, which is a derivative of EΔC71 and lacks cytoplasmic residues 604–615 (see text). Constructs were prepared as previously described (25). (B) PS1 binding to E-cadherin constructs. Extracts (1% digitonin) from L cells (L, lanes 1, 5, and 9) or L cells transfected with mouse E-cadherin (EL, lanes 2, 6, and 10), construct EΔC71 (EΔC71L, lanes 3, 7, and 11), or construct EΔC71Δ604–615 (EΔC71Δ604–615L, lanes 4, 8, and 12) were treated with antibody R222 (lanes 5–8) or anti-p120 antibody (lanes 9–12), and the resulting IPs were probed on WBs with anti-E-cadherin antibody H108. For reference, 20 μg of cell lysates was probed (lanes 1–4). (C) Confluent EL or EΔC71L cells were incubated either with the crosslinking agent dithiobis (succinimidylpropionate) (DSP) in DMSO or with DMSO alone, and cell extracts were then prepared in RIPA buffer in the presence of SDS to inhibit noncovalent associations. Lysates were treated with antibody R222 (R222 IP), and the resulting IPs were probed on WBs with anti-E-cadherin (H108) or anti-PS1/CTF (33B10) antibodies. Twenty micrograms of cell lysate was probed with H108 antibody. (D) PS1 construct Δ340–375 does not bind E-cadherin. HEK293 cells expressing WT PS1 (WT) or a PS1 construct with amino acid deletion 340–375 (Δ340–375) were lysed in TNE plus 1% digitonin. Lysates were treated with anti-E-cadherin antibody (E-cad IP), and the resulting IPs were probed on WBs with antibody 33B10. Twenty micrograms of cell lysates was also probed.