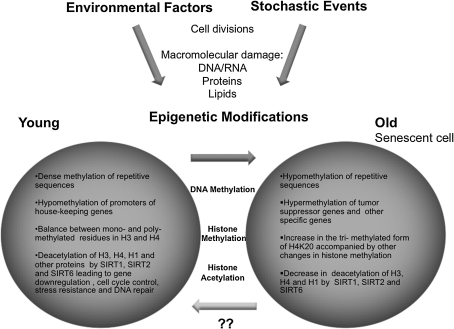
FIG. 6.
Role of epigenetic modifications on aging. The accumulation of cell divisions and macromolecular damage contribute to the aging phenotype. Environmental and stochastic events can further modify this phenotype through epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation, histone methylation, and histone acetylation. The potential reversibility of epigenetic modifications makes them attractive targets for treatment of age-related pathologies.