Figure 2.
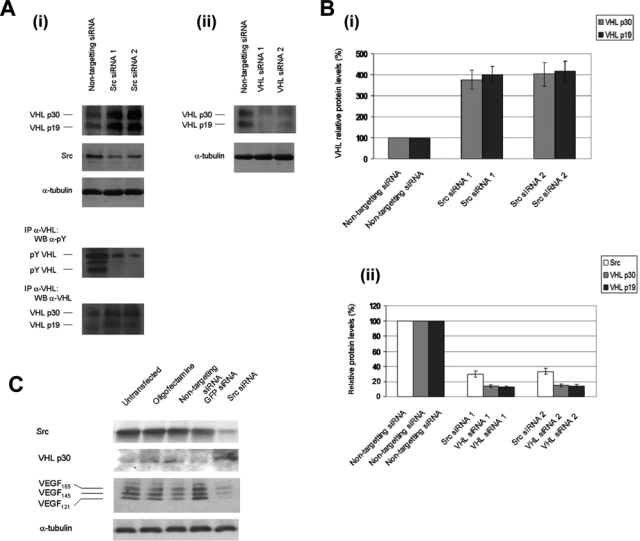
siRNA knockdown of Src increases von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) protein levels. (A) (i, ii) HEK 293T cells were transfected with nontargeting control siRNA, Src siRNA, or VHL siRNA. Forty-eight hours posttransfection, cell lysates were prepared in 2% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), 50 mM Tris (pH 6.8) lysis buffer and boiled, and Western blotting was conducted for endogenous VHL, Src, and α-tubulin. Endogenous VHL protein was also isolated by immunoprecipitation with anti-VHL polyclonal antibody, followed by immunoblotting for phosphotyrosine and VHL. (B) (i) Quantitation of the VHL protein levels of the results from part A. (ii) Quantitation of the knockdown of VHL and Src protein levels of the results from part A. Densitometry was performed using ImageQuant TL software from Amersham Biosciences (Piscataway, NJ). Values were normalized relative to the values for α-tubulin protein levels. Results are representative of n = 3. (C) SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells were transfected with oligofectamine alone (no siRNA), nontargeting control siRNA, green fluorescent protein (GFP) siRNA, or Src siRNA. Conditioned media samples were collected 48 h after transfection and were analyzed by Western blotting for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) using anti-VEGF polyclonal antibody. The conditioned media volumes assayed were corrected for differences in the cell numbers of the cell cultures from which the samples were collected. Western blotting was also conducted on cell lysates using anti-Src monoclonal antibody, anti-VHL polyclonal antibody, and anti-α-tubulin monoclonal antibody. The results are representative of 2 independent experiments.
