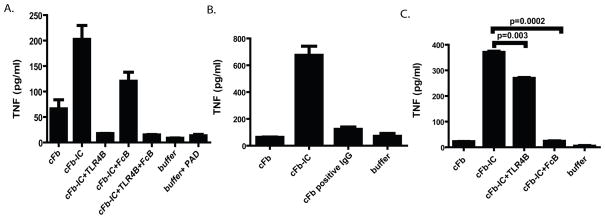
Figure 6.
cFb immune complexes formed with polyclonal anti-Fb antibodies or RA patients’ IgG co-stimulate human macrophages to produce TNF. A, Human monocyte-derived macrophages were pretreated for 30 minutes with the TLR4-inhibitor CLI-095 (1.0 ug/ml), FcγRIIa blocking antibody (10 ug/ml), both inhibitors, or media alone for 30 minutes and then stimulated with cFb (50 ug/ml) or cFb-IC (cFb-IC; 50 ug/ml of cFb incubated with 75 ug/ml of polyclonal anti-Fb antibody). B, Human monocyte-derived macrophages were added to plates pre-coated with citrullinated-fibrinogen immune complexes (cFb-IC) generated using pooled IgG from three RA plasma specimens with high levels of anti-cFb antibodies (Figure 5A, crosshatched bars). Wells coated with nFb incubated with IgG containing anti-cFb antibodies, and plates coated with buffer alone were used as negative controls. C, For assessment of TLR4 dependence and/or FcγR dependence, an identical aliquot of monocyte-derived macrophages was preincubated with the CLI-095 (1.0 ug/ml) or FcγRIIa blocking antibody before being added to the cFb-IC-coated plates. Results are representative of experiments performed at least twice. Values are the mean and SEM of duplicate cultures.