Abstract
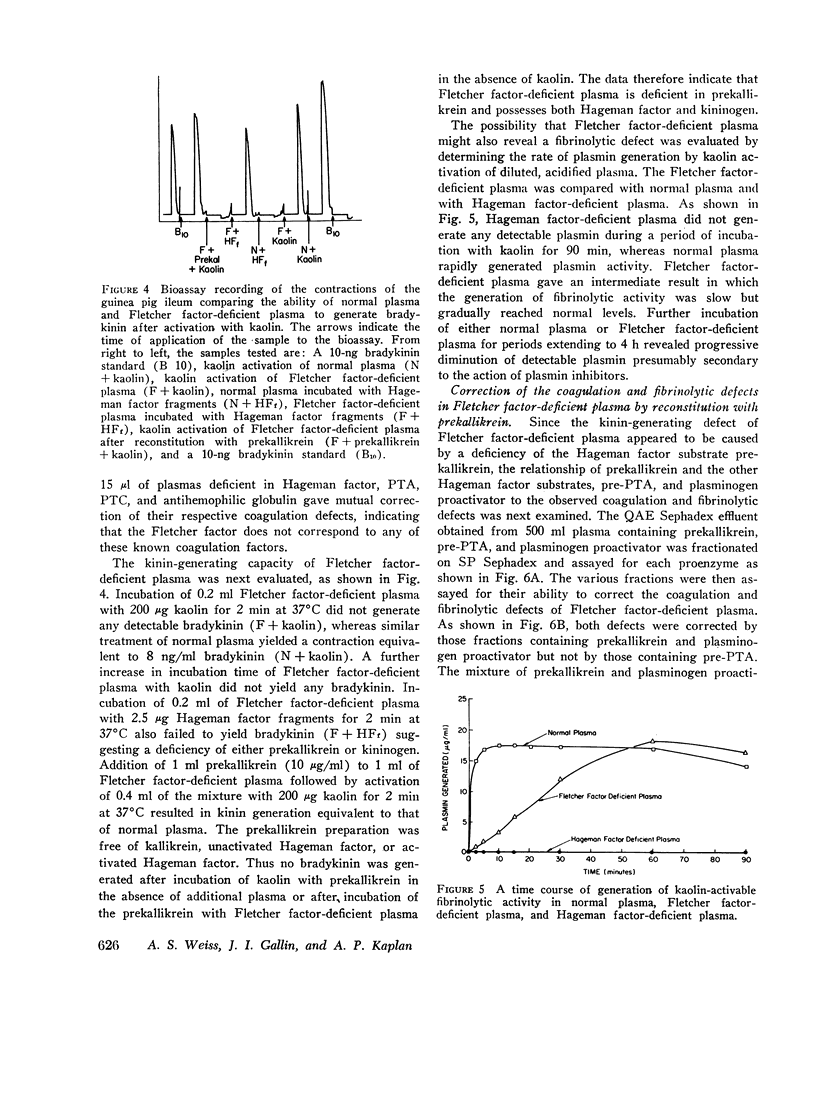
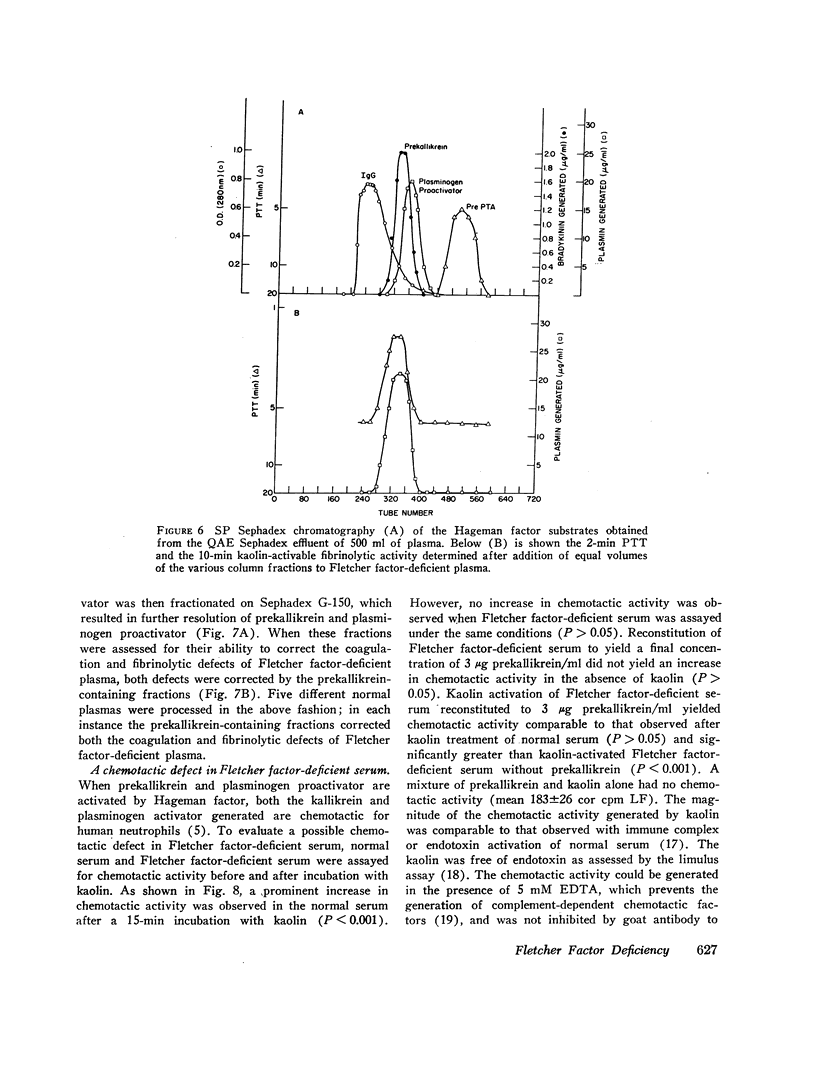
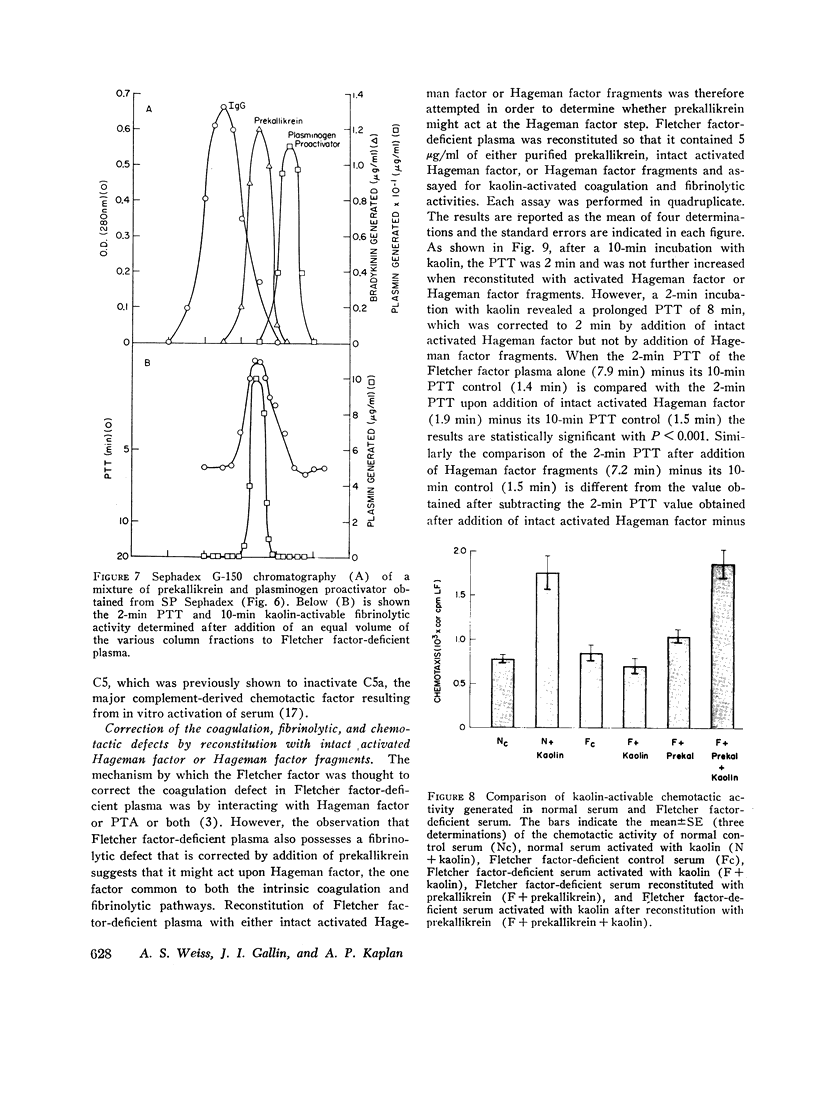
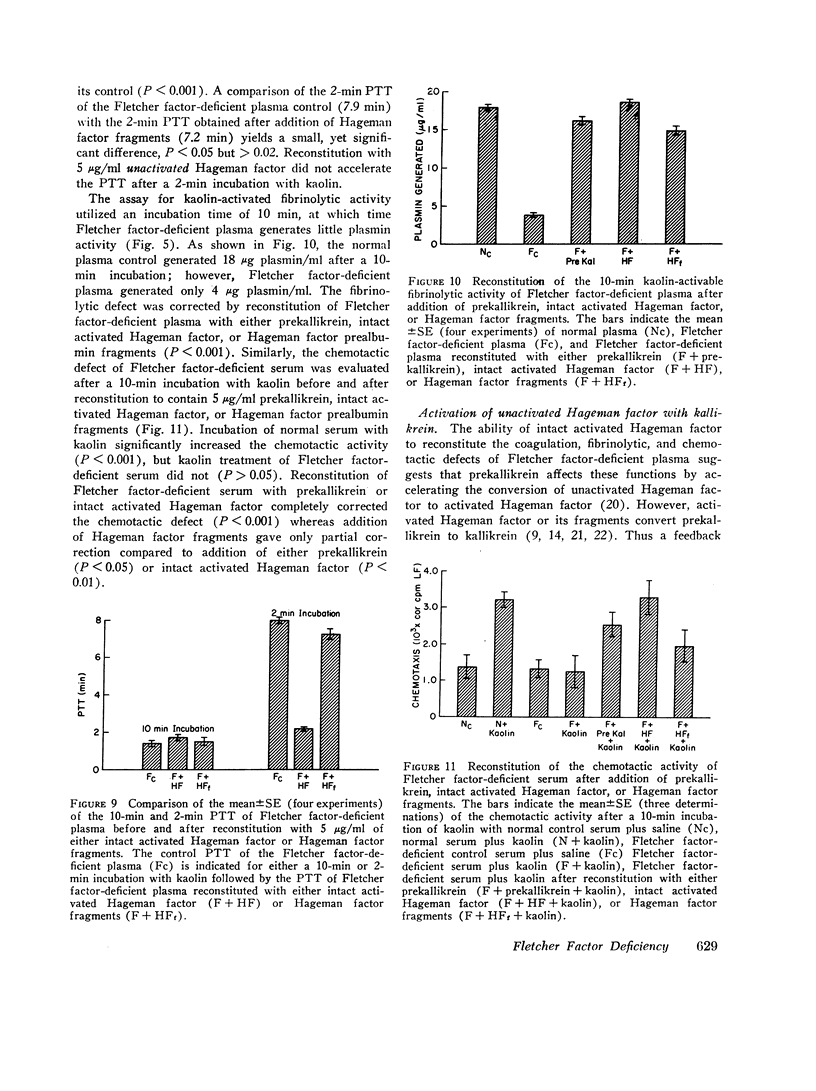
Fletcher factor-deficient plasma is deficient in prekallikrein and therefore generates no bradykinin upon activation with kaolin. It also possesses a diminished rate of kaolin-activable coagulation and fibrinolysis and possesses a defect in kaolin-activable chemotactic activity. These abnormalities are also corrected by reconstitution with purified prekallikrein. Addition of intact activated Hageman factor corrected the coagulation, fibrinolytic, and chemotactic defects and addition of Hageman factor fragments corrected the fibrinolytic defect and partially corrected the chemotactic defect; neither of these corrected the kinin-generating defect. Although the Hageman factor-dependent pathways appear to be initiated by contact activation of Hageman factor, the kallikrein generated activates more Hageman factor; this feedback is necessary for the Hageman factor-dependent pathways to proceed at a normal rate. It is the absence of this feedback in Fletcher factor-deficient plasma that accounts for the diminished rate of activation of Hageman factor and therefore a diminished rate of activation of the coagulation and fibrinolytic pathways. The ability of prekallikrein to correct the coagulation, fibrinolytic, kinin-generating, and chemotactic defects of Fletcher factor-deficient plasma is consistent with the identity of the Fletcher factor and prekallikrein.
Full text
PDF


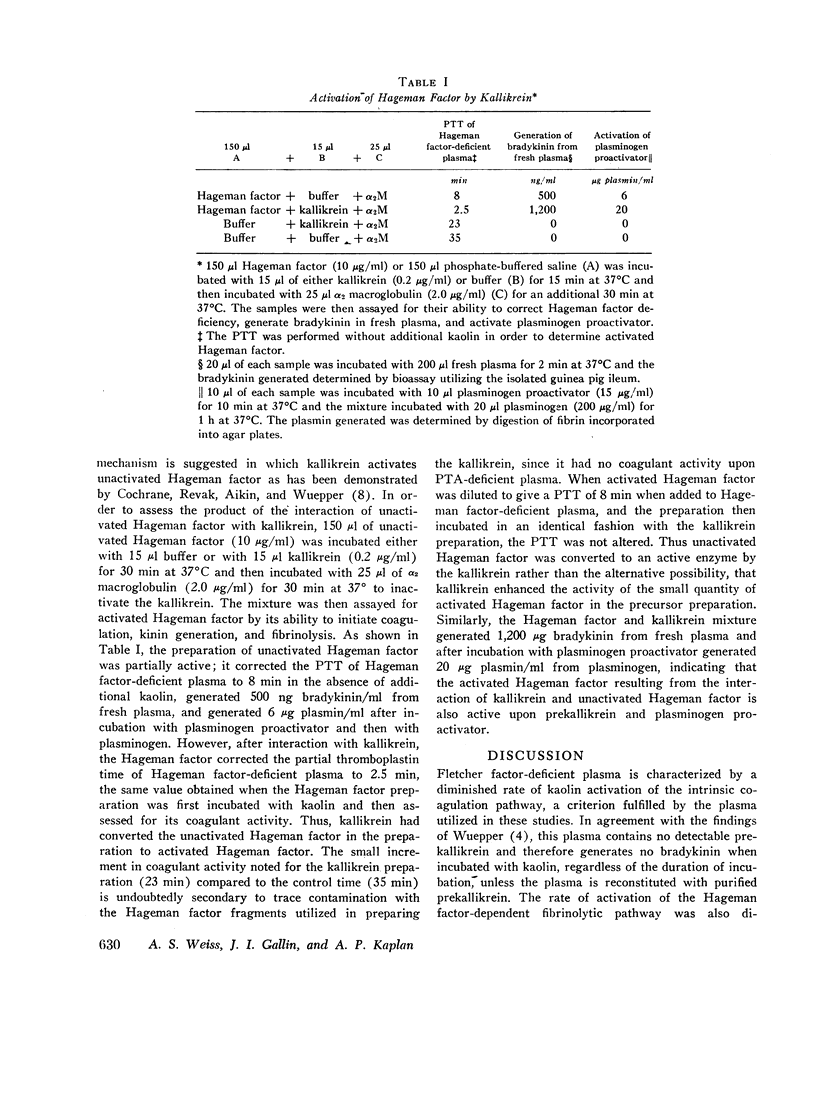

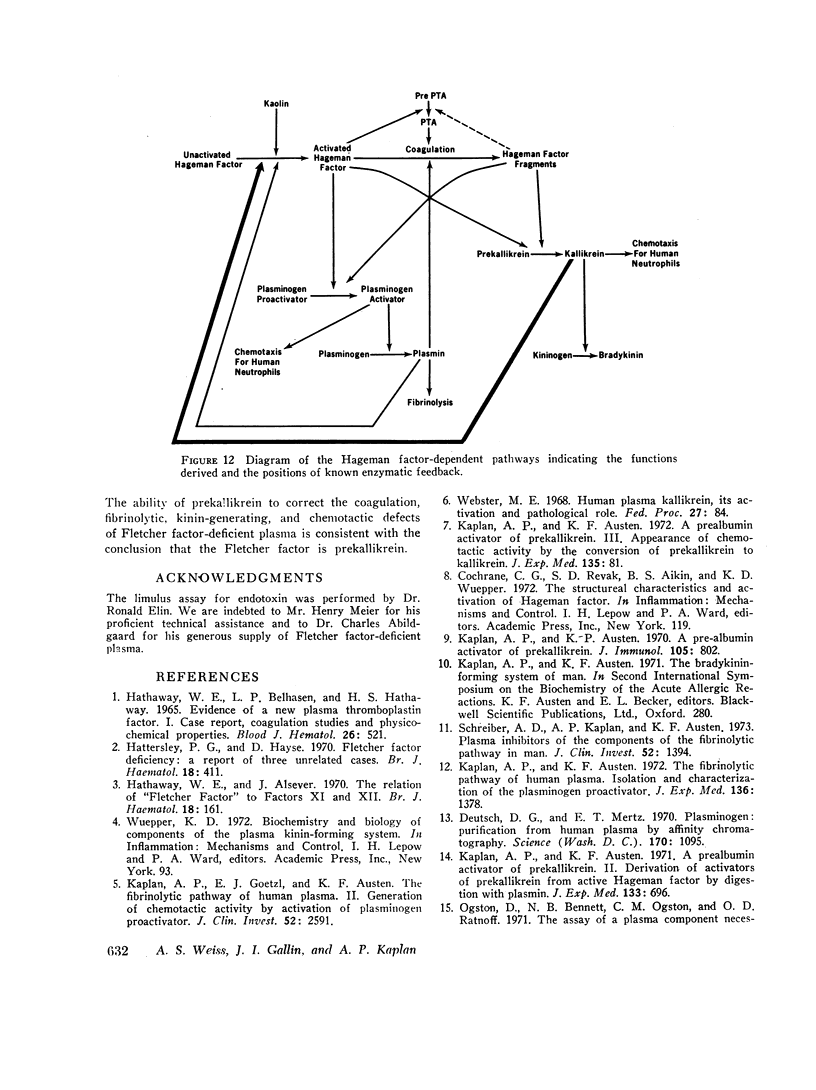

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burrowes C. E., Movat H. Z., Soltay M. J. The kinin system of human plasma. VI. The action of plasmin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Dec;138(3):959–966. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-36027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Wuepper K. D. The first component of the kinin-forming system in human and rabbit plasma. Its relationship to clotting factor XII (Hageman Factor). J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):986–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Clark R. A., Kimball H. R. Granulocyte chemotaxis: an improved in vitro assay employing 51 Cr-labeled granulocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway W. E., Alsever J. The relation of 'Fletcher Factor' to factors XI and XII. Br J Haematol. 1970 Feb;18(2):161–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway W. E., Belhasen L. P., Hathaway H. S. Evidence for a new plasma thromboplastin factor. I. Case report, coagulation studies and physicochemical properties. Blood. 1965 Nov;26(5):521–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattersley P. G., Hayse D. Fletcher factor deficiency: a report of three unrelated cases. Br J Haematol. 1970 Apr;18(4):411–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. A pre-albumin activator of prekallikrein. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):802–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. A prealbumin activator of prekallikrein. II. Derivation of activators of prekallikrein from active Hageman factor by digestion with plasmin. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):696–712. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. The fibrinolytic pathway of human plasma. Isolation and characterization of the plasminogen proactivator. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1378–1393. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Kay A. B., Austen K. F. A prealbumin activator of prekallikrein. 3. Appearance of chemotactic activity for human neutrophils by the conversion of human prekallikrein to kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):81–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogston D., Bennett N. B., Ogston C. M., Ratnoff O. D. The assay of a plasma component necessary for the generation of a plasminogen activator in the presence of Hageman factor (Hageman factor co-factor). Br J Haematol. 1971 Feb;20(2):209–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb07029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patten E., Gallin J. I., Clark R. A., Kimball H. R. Effects of cell concentration and various anticoagulants on neutrophil migration. Blood. 1973 May;41(5):711–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. Plasma inhibitors of the components of the fibrinolytic pathway in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1394–1401. doi: 10.1172/JCI107312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltay M. J., Movat H. Z., Ozge-Anwar A. H. The kinin system of human plasma. V. The probable derivation of prekallikrein activator from activated Hageman factor (XIIa). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Dec;138(3):952–958. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-36026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster M. E. Human plasma kallikrein, its activation and pathological role. Fed Proc. 1968 Jan-Feb;27(1):84–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin E. T., Galanos C., Kinsky S., Bradshaw R. A., Wessler S., Lüderitz O., Sarmiento M. E. Picogram-sensitive assay for endotoxin: gelation of Limulus polyphemus blood cell lysate induced by purified lipopolysaccharides and lipid A from Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 28;261(1):284–289. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90340-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]