Figure 2.
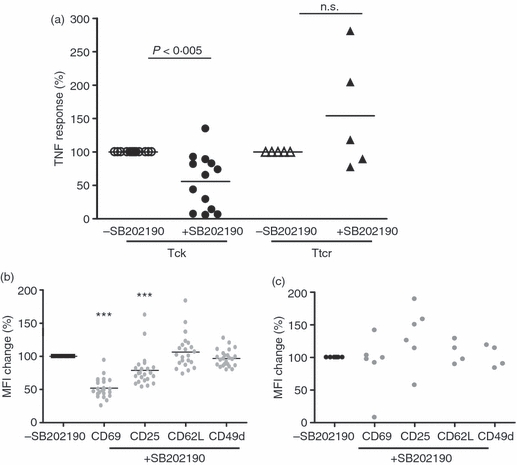
Early p38 activity regulated the effector function of cytokine-activated T (Tck) cells but not anti-CD3 activated T (Ttcr) cells. CD4+ CD45RO+ T cells were stimulated with interleukin-2 (IL-2)/IL-6/tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) for 8 days or with plate-bound anti-CD3 for 48 hr. Each symbol represents an individual donor. All results are presented as a percentage change of those generated without SB202190. (a) The ability of Tck ± SB202190 and Ttcr ± SB20219 to activate monocytes was determined by TNF-α produced after co-culture with autologous monocytes for 18 hr. Tck versus Tck + SB202190: n = 13, P < 0·005; Ttcr versus Ttcr + SB202190: n = 5, not significant. (b) Change of CD69, CD25, CD62L and CD49d expression on Tck ± SB202190. n = 23. p38 inhibition significantly down-regulated mean fluorescence intensity of CD69 (P < 0·0001) and CD25 (P < 0·0005). (c) Expression of CD69 (n = 6), CD25 (n = 6), CD49d (n = 4) and CD62L (n = 4) were not significantly modulated by SB202190 in Ttcr cells.
