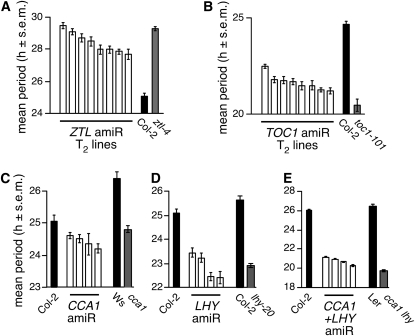
Figure 3.
Targeted Knockdowns of Arabidopsis Clock Genes by amiRNAs.
amiRNAs (Schwab et al., 2006) were designed to target each of the clock genes CCA1, LHY, TOC1, and ZTL. Randomly chosen T2 transgenic lines were characterized for the period of the circadian reporter CCA1pro:LUC, which is present in the same T-DNA as the 35S:amiRNA cassette (see Methods for details). All data (luciferase activity and circadian periods) are shown as mean ± se (s.e.m.; n = 12).
(A) Mean period length for ZTL amiRNA lines. The period length of TOC1pro:LUC in the T-DNA insertion allele ztl-4 (Michael et al., 2003) is shown as reference.
(B) Mean period length for TOC1 amiRNA lines and the corresponding loss-of-function phenotype in the toc1-101 mutant (Kikis et al., 2005).
(C) Mean period length for CCA1 amiRNA lines. Note that no true loss-of-function allele exists for CCA1 in the Col-0 background. Ws, Wassilewskija.
(D) Mean period length for LHY amiRNA lines and the corresponding loss of function phenotype in the lhy-20 T-DNA insertion allele (Michael et al., 2003).
(E) Mean period length for CCA1-LHY tandem amiRNA lines. Ler, Landsberg erecta.