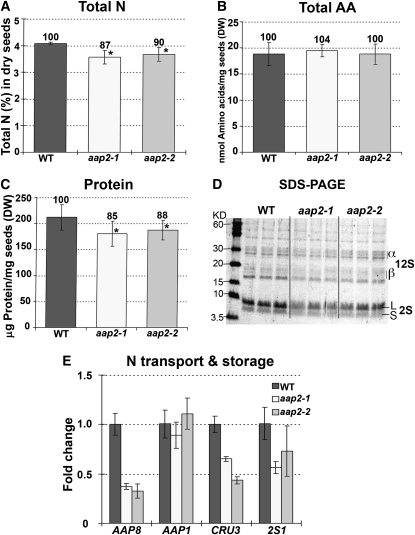
Figure 5.
Seed N Levels and Expression of Genes Involved in N Transport and Metabolism in Seeds of Wild-Type and aap2 Plants.
Error bars depict sd. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type (WT; P < 0.05). Values above the columns indicate the percentage compared with the wild type, which was set to 100%. DW, dry weight.
(A) Total N levels (%) in dry seeds (n = 4).
(B) Total free amino acids (AA) in dry seeds (n = 4).
(C) Total amount of soluble proteins in dry seeds (n = 5).
(D) SDS-PAGE analysis of soluble proteins in dry seed. Three technical repetitions from independent extractions were done for each line as shown. α- and β-subunits of storage protein 12S globulin. S and L, small and large subunits of the 2S albumin storage protein.
(E) Real-time PCR analysis of genes of N transport and storage in developing seeds. Expression of amino acid transporter AAP8 (At1g10010) and AAP1 (At1g58360) as well as CRU3 (At4g28520) and 2S1 (At4g27140) encoding for 12S globulin and 2S albumin, respectively, were analyzed. Three technical repetitions were done for each line using Arabidopsis ubiquitin 11 (UBQ11, At4g05050) and tubulin β-9 chain (TUB9, At4g20890), respectively, as control genes. Shown is the fold change in gene expression relative to UBQ11 expression, determined from the CT values using the 2–ΔΔCT method (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001).