Figure 2.
Sgd-1 Is Caused by an Intragenic Mutation at the GID1 Locus.
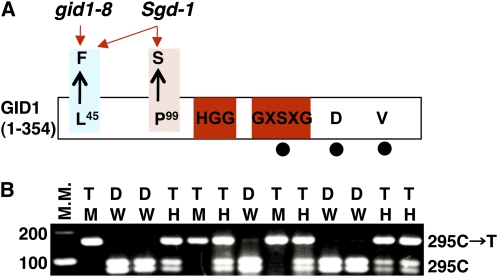
(A) Schematic structure of GID1 indicating the positions of the gid1-8 mutation (L45→F), which is present in both gid1-8 and Sgd-1, and the Sgd-1 mutation (P99→S), which is present only in the Sgd-1 suppressor mutant. Amino acid residues shared with HSL, such as HGG and GXSXG, are shown within red boxes. The residues corresponding to the catalytic triad of HSL, S, D, and V, are indicated by filled circles.
(B) Linkage analysis between the Sgd-1 phenotype and the P99S mutation in the M2 generation of Sgd-1. The P99S mutation is caused by an SNP (C295T), which introduced a cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence polymorphism after digestion with HaeIII. Plants homozygous for the wild type or mutant allele at this SNP are designated as W or M, respectively, and heterozygous plants are designated as H. Plants showing the dwarf (D) phenotype of gid1-8 are designated as D, and plants showing the taller (T) phenotype of Sgd-1 are designated as T. All plants carrying the M and H genotypes showed the Sgd-1 phenotype (T), while plants carrying the W genotype showed the gid1-8 phenotype (D), indicating complete linkage between the Sgd-1 phenotype and the P99S mutation. M.M., molecular marker.