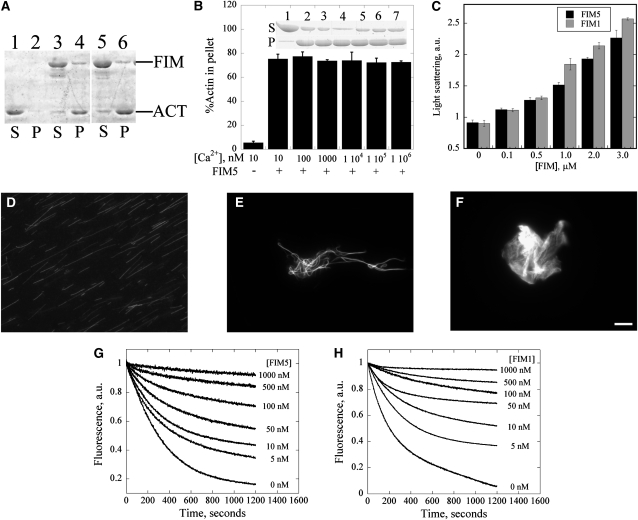
Figure 10.
FIM5 Bundles and Stabilizes Actin Filaments.
(A) A low-speed cosedimentation assay was employed to assess the actin bundling activity of FIM5. Lanes 1 and 2 contain actin alone, lanes 3 and 4 contain actin +1 μM FIM1, and lanes 5 and 6 contain actin + 1 μM FIM5. S, supernatant; P, pellet.
(B) FIM5 bundles actin filaments in a calcium-insensitive manner. F-actin (3 μM) was incubated with 1 μM FIM5 in the presence of the indicated concentrations of free calcium. Graph shows the percentage of sedimented actin for each [Ca2+]free value. Error bars represent ± se. Inset: SDS-PAGE gel showing the amount of actin in the supernatant and pellet in the presence of the indicated concentrations of Ca2+ after sedimentation at 13,600g for 30 min at 4°C.
(C) A light scattering assay was used to characterize the formation of higher-order actin structures induced by FIM5. The absorbance of the mixture was monitored at 400 nm after 3 μM preassembled actin filaments were incubated with the indicated concentrations of FIM5 (black) or FIM1 (gray) for 30 min at room temperature. Error bars represent ± se.
(D) to (F) Cross-linking of actin filaments was visualized directly by fluorescence microscopy for samples containing actin alone (D), actin + 1 μM FIM5 (E), and actin + 1 μM FIM1 (F). Bar = 5 μm.
(G) and (H) FIM5 and FIM1 inhibit dilution-mediated actin depolymerization. Graphs show representative results for the indicated concentrations of FIM5 (G) and FIM1 (H). a.u., arbitrary units.