Figure 2.
Inhibition of Protease Activity in E. coli FtsH with Amino Acid Substitutions.
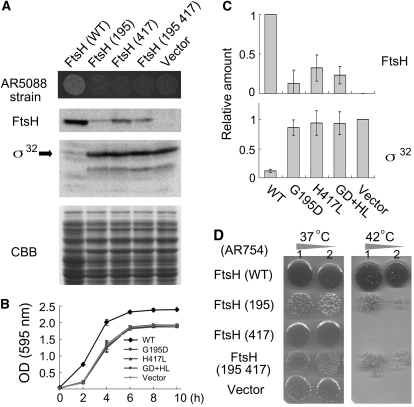
(A) In vivo protease activity of wild-type and mutant FtsH proteins in E. coli. AR5088 (sfhC ΔftsH) was transformed with pIFH108 containing wild-type FtsH (WT) or containing mutated FtsHs (G195D, H417L, or G195D+H417L). Vector indicates an empty vector without FtsH. Cells harboring plasmids of mutated FtsHs (G195D, H417L, and G195D+H417L) or without FtsH displayed smaller colonies, reflecting deficient growth (top panel). Immunoblots of E. coli extracts with anti-FtsH and anti-σ32 (a substrate of FtsH) are shown together with the CBB-stained gel image of the same samples.
(B) Growth curves of E. coli AR5088. Cells transformed with empty vector pER15b (Vector) or with pIFH108 expressing wild-type FtsH or mutated FtsHs (G195D, H417L, and G195D+H417L [abbreviated as GD+HL]) were grown in LB medium. Cell densities of bacteria were measured according to photometric detection with OD (595 nm) readings (bars represent sd; five biological repeats).
(C) Relative amounts of FtsH and σ32 estimated by immunoblotting (bars represents sd; six biological repeats). To normalize the expression values, the pIFH108 (WT) and empty vector control values were set to 1 for FtsH and σ32, respectively
(D) Complementation of ftsH1 (Ts) by wild-type and mutated FtsH proteins. ftsH1 (AR754) is a temperature-sensitive mutant that was transformed with pIFH108 containing FtsH (WT), FtsH (195), FtsH (417), or FtsH (195 417) or without an insert (Vector). Growth of each strain on LB agar at 37°C (left) and 42°C (right) is shown. Rows 1 and 2 present data of 1-fold and 10-fold dilutions of cultures, respectively.