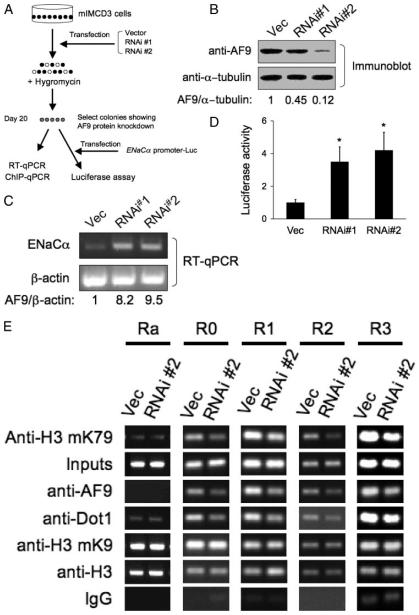
FIGURE 4. RNA interference knockdown of AF9 expression impairs AF9, Dot1, and histone H3 Lys-79 methylation associated with the ENaCα promoter and increases expression of endogenous ENaCα and the activity of the ENaCα promoter-luciferase construct.
A, diagram of the experiment procedure. B, immunoblots showing knockdown of AF9. Three independently mIMCD3 cell lines stably transfected with pSilencer 2.1-U6-hygro negative control (Vec), pAF9-RNAi#1 (RNAi#1), or pAF9-RNAi#2 (RNAi#2) were examined by immunoblotting with the chicken AF9 antibody or the anti-α-tubulin antibody. The normalized AF9 level (to the α-tubulin abundance) is shown with the AF9 of the vector-transfected cells arbitrarily setto 1. C, RT-qPCR showing that knockdown of AF9 increases ENaCα mRNA levels. The same cell lines as in B were examined with realtime RT-qPCR for expression of ENaCα or β-actin as control. n = 3. D, the same cells as in B were transiently transfected with pGL3Zeocin-1.3ENaCα, followed by luciferase assay as described in the legend to Fig. 3B. *, p < 0.05 versus Vec, n = 3. E, ChIP assay showing that knockdown of AF9 decreased occupancy of AF9, Dot1, and histone H3 Lys-79 methylation in the ENaCα promoter. The same cells as in B were subjected to ChIP assay as in Fig. 3D, except for the use of the rabbit antibodies specific for Dot1 or AF9. n = 3.