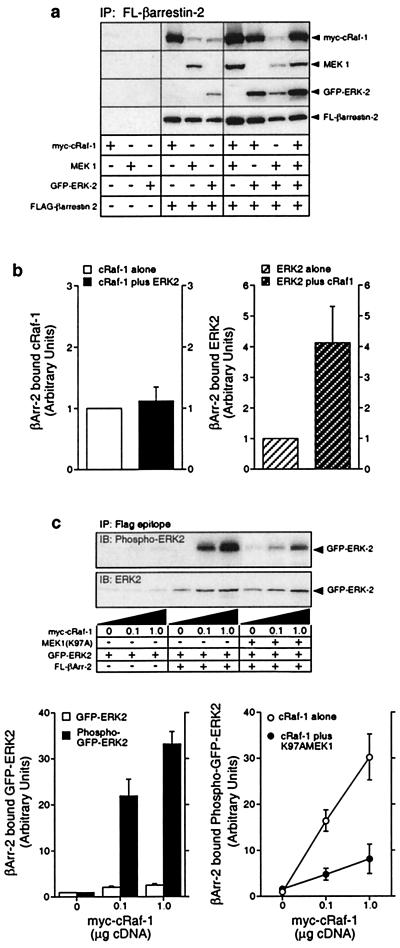
Figure 3.
Binding of myc-cRaf-1, MEK1 and activated GFP-ERK2 to wild-type and mutant Flag-β-arrestin-2. (a) COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with plasmid DNA encoding myc-cRaf-1, MEK1, GFP-ERK2, and Flag-β-arrestin-2 in various combinations as indicated. GFP-ERK2, which undergoes agonist-stimulated phosphorylation and nuclear translocation like the wild-type kinase (10; not shown), was used in these studies to allow each overexpressed protein to have a unique epitope tag. Anti-Flag immunoprecipitates were probed for coprecipitated cRaf-1, MEK1, ERK2, and β-arrestin-2. Equivalent expression of each construct was confirmed by immunoblotting an aliquot of each whole cell lysate in parallel (not shown). Shown are representative immunoblots from one of six separate experiments. (b) Bar graphs depict the amount of myc-cRaf-1 (Left) and GFP-ERK2 (Right) present in Flag-β-arrestin-2 immunoprecipitates from cells coexpressing myc-cRaf-1 only, GFP-ERK2 only, or both myc-cRaf-1 and GFP-ERK2. Data are presented in arbitrary units where the amount of myc-cRaf-1 or GFP-ERK2 binding to Flag-β-arrestin-2 when singly expressed is defined as 1. Data shown represent the mean ± SD from four separate experiments. (c) Cells were transiently transfected with plasmid DNA encoding GFP-ERK2 and increasing amounts of myc-cRaf-1, in the presence and absence of Flag-β-arrestin-2 and MEK(K97A) as indicated. The amount of GFP-ERK2 and phospho-GFP-ERK2 present in Flag-β-arrestin-2 immunoprecipitates was determined by immunoblotting (Upper). Graphs depict the amount of GFP-ERK2 and phospho-GFP-ERK2 present in Flag-β-arrestin-2 immunoprecipitates (Left) and the effect of MEK(K97A) expression on the amount of phospho-GFP-ERK2 present in Flag-β-arrestin-2 immunoprecipitates (Right). Data are presented in arbitrary units where the amount of GFP-ERK2 or phospho-GFP-ERK2 present in Flag-β-arrestin-2 immunoprecipitates in the absence of overexpressed myc-cRaf-1 is defined as 1. Data shown represent the mean ± SD from three separate experiments.