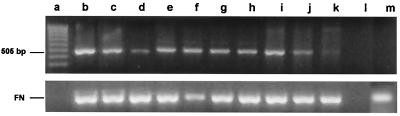
Figure 2.
Reverse transcription–PCR analysis of vasa mRNA in zebrafish embryo cell cultures. cDNA was synthesized from total RNA obtained from embryo cell cultures. PCR amplification was performed with vasa-specific primers designed to generate a 505-bp product. Product identity was confirmed by sequencing. Lane a, MW markers; lanes b, c, and d, embryo cells maintained for 5, 15, and 25 days, respectively, in RTS34st cell-conditioned medium; lanes e, f, and g, embryo cells maintained for 5, 15, and 25 days, respectively, on an RTS34st feeder layer; lane h, embryo cells maintained at first for 24 days in RTS34st cell-conditioned medium, and then (after passaging) for 8 days on an RTS34st feeder layer; lanes i, j, and k, embryo cell cultures maintained for 1, 3, and 5 days, respectively, in the absence of RTS34st feeder cells or cell-conditioned medium; lane l, negative control (no template); lane m, RTS34st cells cultured in the absence of zebrafish embryo cells. Primers that amplify fibronectin cDNA were used to control for equal amounts of sample in each lane.