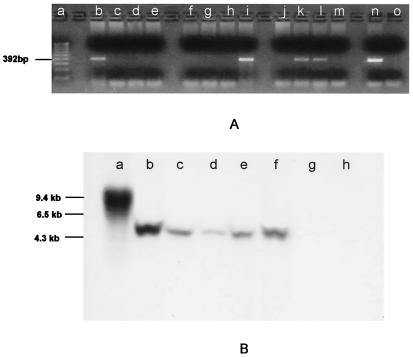
Figure 4.
PCR (A) and Southern blot analysis (B) of genomic DNA showing the presence of neo sequences. (A) Genomic DNA isolated from individual F1 fish (lanes b–m) produced from a single spawning of GASSI fish that were injected as embryos with cultured cells and bred with noninjected GASSI individuals. DNA was amplified with neo-specific primers designed to generate a 392-bp product. Product identity was confirmed by sequencing. neo sequences were detected in lanes b, i, k, and l. Lanes a, n, and o are molecular weight markers, positive control (neo-containing plasmid template) and negative control (no template), respectively. (B) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA by using a neo-specific probe. The same integration pattern for neo sequences was observed in DNA isolated from B7–43 fish (lane b), cell cultures derived from B7–43 embryos (lane c), individual F1 fish (lanes d and e) obtained from a GASSI chimera that was injected at the blastula stage with cultured B7–43 embryo cells and bred with a noninjected GASSI fish, and an F2 individual (lane f) obtained by breeding positive F1 siblings. Lane a, DNA isolated from fish embryo cells transfected in culture with neo-containing plasmid showing a different integration pattern. Lanes g and h, DNA isolated from a GASSI fish and another nontransgenic line of zebrafish.