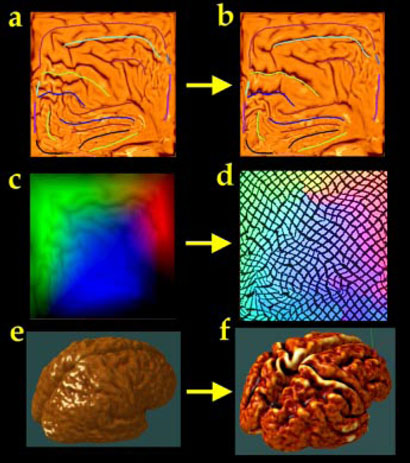
Fig. 1. Averaging Cortical Models.
A well-resolved average cortical model (f) for a group of subjects can be created by first flattening each subject's cortical model to a 2D square (a). A color coded map (c) stores a unique color triplet (RGB) at each location in the 2D parameter space encoding the (x,y,z) coordinate of the 3D cortical point mapped to that 2D location. However, a well-resolved average model (f) is produced, with cortical features in their group mean location, if each subject's color map is first flowed (d) so that sulcal features are driven into the configuration of a 2D average sulcal template (b). Codes indexing similar 3D anatomical features are placed at corresponding locations in the parameter space, and are thus reinforced in the group average (f).