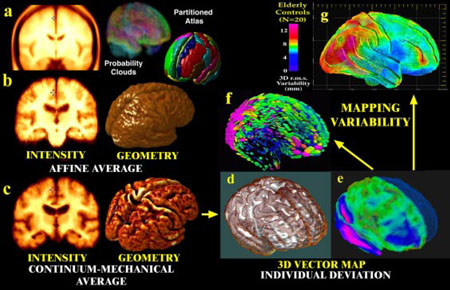
Fig. 2. Probabilistic Modeling of Brain Anatomy.
Direct averaging of imaging data after a simple affine transform into stereotaxic space washes cortical features away((a); Evans et al., 1994; N=305 normals); (b) a similar approach with N=9 Alzheimer's patients). By first averaging a set of vector-based 3D geometric models, and warping each subject's scan into the average configuration, a well-resolved average brain template is produced (c). Deformation vector maps (e) store individual deviations (brown mesh) from a group average (white surface, (d)), and their covariance fields (f) store information on the preferred directions and magnitude (g) of anatomic variability(pink colors, large variation; blue colors, less).