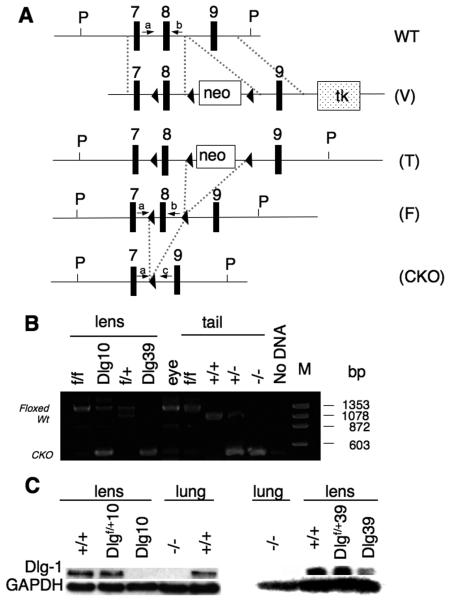
Figure 1. Generation of Dlg-1 conditional mutant mice.
A: Diagram showing the targeting vector and steps to generate the Dlg-1 conditional knockout. Shown is a portion of the WT allele highlighting exons 7-9 and arrows to indicate the location for PCR primers a and b (see Table 1, PCR primer combination 1, primer a=Dlg 5′ forward and primer b=Dlg8R reverse) for genotyping. The targeting vector (V) is shown, indicating lox P sites (arrowheads), placement of the positive selection neomycin marker (neo) and the negative selection Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (tk) marker after exon 9. Shown is the targeted allele (T) carried by the correctly targeted ES cell clones that were used to generate chimeras. Shown is the floxed allele (F), which was generated after mating to EIIAcre mice to remove the neo marker is shown. Arrows indicate locations for PCR primers a and b (See Table 1, primer combination 1), which were used for routine genotyping of the mice. Finally, the conditional knockout (CKO) allele is shown, which results from lens specific cre induced deletion of exon 8. Arrows indicate locations of PCR primers a and c (see Table 1, PCR primer combination 2, primer c=Dlg 3′ reverse) which were used to verify that exon 8 had been deleted specifically in lens DNA. B: Lens-specific cre mediated deletion of exon 8. PCR primers a and c were used to amplify DNA fragments from lens and tail samples of mice with the indicated genotypes. The band representing the wild type allele is 1058 bp while the band representing the floxed alleled is 1273 bp. The 380 bp band representing the deleted allele is observed when PCR was carried out on DNA from Dlg-1 mutant lenses, and on tail samples from mice heterozygous or homozygous for the germline null allele. C: Western blot analysis from whole lens (Dlg10) or fiber extracts (Dlg39) from P2 mice of the indicated genotypes showing reduced levels of Dlg-1 in lenses from CKO mice as compared to a GAPDH loading control. To demonstrate the specificity of the antibody, protein extracts from Dlg-1+/+ and Dlg-1−/− lung samples were blotted at the same time.