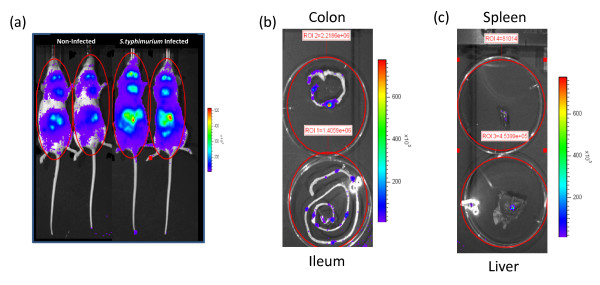
Figure 1.
Biophotonic imaging of S. typhimurium induced NF-κB activation. Following 4 hours of infection with S. typhimurium in mice fed control diets, whole body biophotonic imaging revealed a significant increase in NF-κB activation. Two representative animals are illustrated (a). Isolated gastrointestinal tissue from S. typhimurium-infected animals displays enhanced NF-κB activation within the ileum and colon (b). Isolated spleen and liver tissue also display NF-kB activity following S. typhimurium infection (c). The region of interest (ROI) is shown with the photons/sec/cm2 value for representative ROI included.