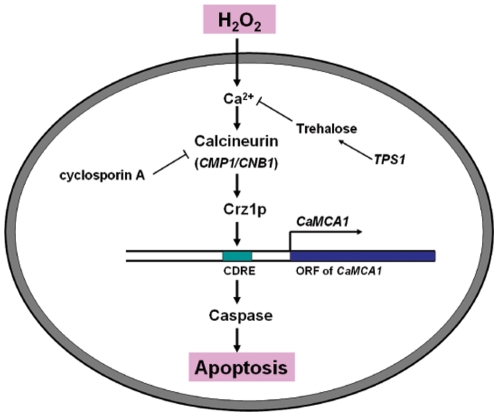
Figure 5. A model for the role of trehalose in the regulation of H2O2-induced apoptosis in C. albicans.
When C. albicans is exposed to H2O2, the intracellular Ca2+ is increased and its downstream calcineurin/Crz1p pathway is activated. The calcineurin inhibitor cyclosporin A can block this pathway. Crz1p might up-regulate the expression of CaMCA1 through binding to the CDRE (calcineurin-dependent responsive element) in the promoter of CaMCA1. The increased expression of CaMCA1 results in the increased caspase activity and thus apoptosis occurs. tps1△ mutation results in the lack of trehalose accumulation thus accelerates C. albicans apoptosis.