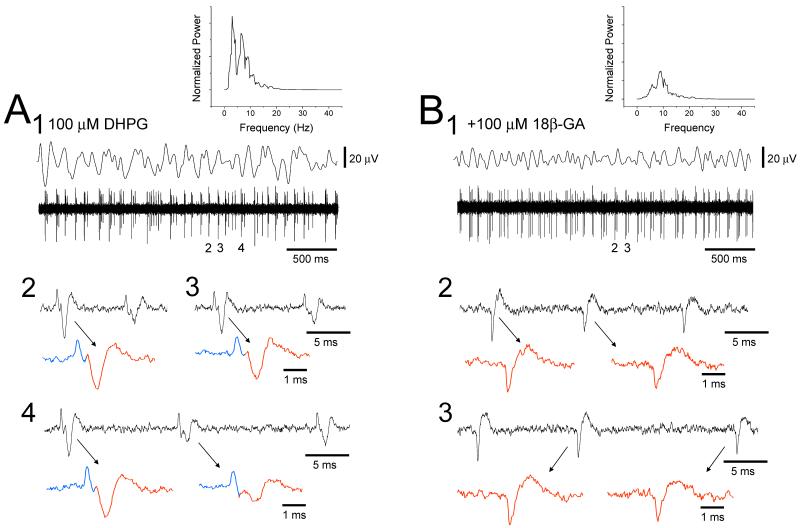
Figure 5. GJ blockers suppress field oscillations and neuronal synchrony.
A. Simultaneous field and unit recording from the cat LGN slice in the presence of 100 μM DHPG showing coherent rhythmic activity (corresponding power spectrum is in the top right). Close examination of the unit recording reveals two closely synchronized neurons (enlarged and shown in blue and red). B. The putative GJ blocker, 18-β glycyrrhetinic acic (18-β GA, 100 μM), greatly suppresses the field oscillation (see corresponding power spectrum in the top right) and abolishes the synchronized firing.