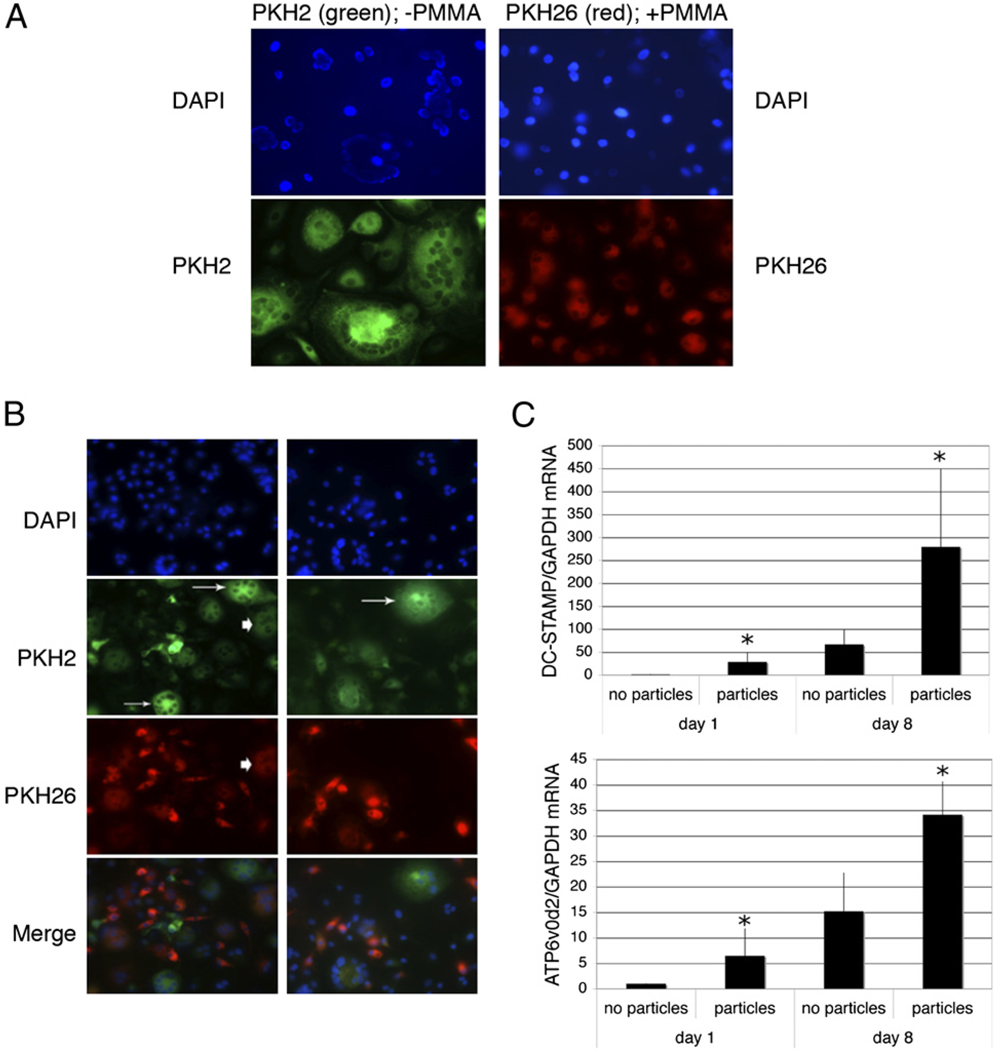
FIGURE 4.
Particle phagocytosis prevents initiation of osteoclastogenesis but does not eliminate fusion with developing osteoclasts. A and B, Preosteoclasts were cytoplasmically labeled with PKH2 (green) or allowed to phagocytose PMMA particles and then labeled with PKH26 (red). The two cell populations were then cultured in the presence of 25 ng/ml M-CSF and 50 ng/ml RANKL either alone (A; original magnification ×50) or as cocultures (B; original magnification ×25). Equivalent results were obtained in three separate experiments. Osteoclasts formed exclusively from particle-free cells are indicated by arrows, and osteoclasts that have incorporated both particle-free and particle-containing cells are indicated with arrowheads. C, Preosteoclasts were cultured for 1 and 8 d with and without PMMA particles (20 particles/cell) in medium supplemented with 25 ng/ml M-CSF. RNA was extracted and DC-STAMP and ATP6v0d2 expression measured by qPCR. DC-STAMP and ATP6v0d2 mRNA levels expressed relative to GAPDH were normalized to the day 1 samples without particles. n = 5. *p < 0.05 compared with equivalent sample without particles.