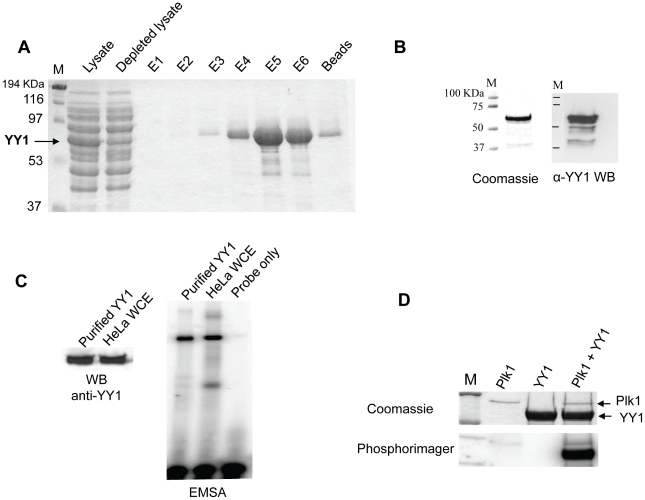
Figure 1. Plk1 phosphorylates YY1 in vitro.
(A) Coomassie blue staining of SDS-PAGE gel showing the purification of bacterially expressed non-tagged YY1 under denaturing conditions. An arrow indicates the position of overexpressed YY1. Lysates: sample from total bacterial lysates; Depleted lysates: sample from bacterial lysates after passing through the Ni-NTA column. E1, 2, and 3 are samples from elutions at pH 5.9; E4, 5, and 6 are samples from elutions at pH 4.5; the last lane shows a sample of the Ni-NTA beads after the last elution step. (B) Coomassie blue staining (left panel) and Western blot analysis (right panel) of purified YY1 after renaturation, and separation by SDS-PAGE. In the Western blot, YY1 was probed with anti-YY1 (H-10) antibody. (C) EMSA testing the DNA binding activity of purified and renatured YY1 side by side with HeLa whole cell extract. A 22 bp oligonucleotide encompassing the YY1 binding site in histone H3.2 coding region was used as the radioactively labeled probe. The Western blot shows equal amounts of purified YY1 and YY1 protein in HeLa WCEs. (D) Coomassie blue staining and phosphorimager exposure of SDS-PAGE gel after radioactive in vitro kinase assay, using purified Plk1 and YY1. The gel shows three reactions: Plk1 only, YY1 only, and Plk1 plus YY1; as indicated.