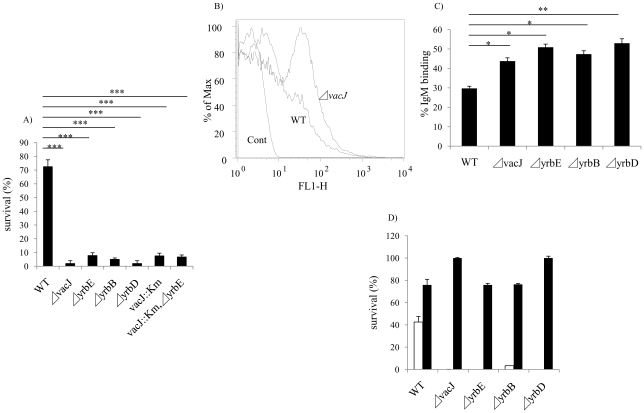
Figure 2. Characterization of vacJ and yrb mutants.
(A) Effect of mutations in vacJ and genes of the yrb ABC transporter on serum resistance of strain R2866. Survival was determined over 60 min in 5% normal human serum and expressed relative to controls in which complement was inactivated. (B) Representative histogram comparing the binding, as measured by fluorescence intensity (x-axis), of total IgM purified from normal human serum to parent strain (WT) or vacJ by flow cytometry. Control performed without IgM (C) Percent IgM binding for each mutant was determined by calculating the percentage of 50,000 events with an increase in mean fluorescence intensity following incubation in 5% heat-inactivated normal human serum compared to no serum controls. (D) Survival of mutants in 10% normal human serum in the presence (black bars) or absence (white bars) of Mg-EGTA to inhibit the classical pathway of complement activation. Values represent two independent experiments in triplicate ± SD. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001.