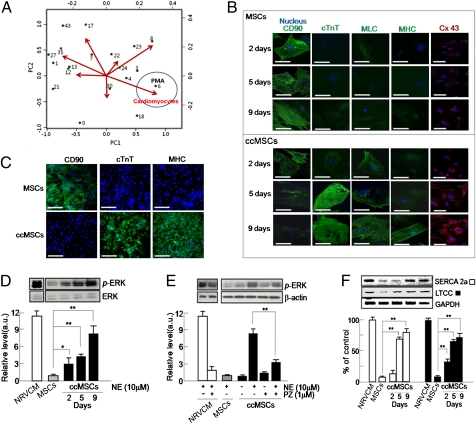
Fig. 2.
Characterization of ccMSCs. (A) Principal component analysis (PCA) for small molecule-induced modification of MSCs. We obtained the coordinates of chemicals and target cell types by using the first two principal components from PCA and scaled the two sets of coordinates to plot them together in the map. The two largest principal components of PCA analysis are represented as PC1 and PC2. The spheres attached to the longer vectors are more efficient differentiation inducers for the cell types. The chemicals tested are indicated by green spheres (PMA is shown in blue) and the specific cell lineages are shown as red arrows. Tested molecules are from Calbiochem and are distinguished by numerals as follows: 0, no inhibitor; 1, 1,3-dihydro-1-(1-((4-(6-phenyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-g]quinoxalin-7-yl)phenyl)methyl)-4-piperidinyl)-2H-benzimidazol-2-one; 2, 1L6-hydroxymethyl-chiroinositol-2-(R)-2-O-methyl-3-O-octadecyl-sn-glycerocarbonate; 3, SH-5 ([(2R)-2-methoxy-3-octadecoxypropyl] (2,3,4-trihydroxy-6-methoxycyclohexyl) hydrogen phosphate); 4, lavendustin (5-(N-2′,5′-dihydroxybenzyl) aminosalicylic acid); 6, PMA (phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate); 7, DMAT (2-dimethylamino-4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-1H-benzimidazole); 8, D4476 (4-(4-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-5-pyridin-2-yl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)benzamide); 12, NU6102 [6-cyclohexylmethoxy-2-(4′-sulfamoylanilino)purine]; 13, [3-(pyridin-2-yl)-4-(4-quinonyl)]-1Hpyrazole; 17, H-89 [N-[2-((p-bromocinnamyl)amino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide, 2HCl]; 18, SH-6 ([(2R)-2-methoxy-3-octadecoxypropyl] (2,3,4-trihydroxycyclohexyl) hydrogen phosphate); 21, Gö6983 (2-[1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-5-methoxyindol-3-yl]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)) maleimide; 22, guanosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphorothioate, β-phenyl-1, N2-etheno-8-bromo-, Rp-isomer, sodium salt; 23, compound 56 (4-[(3-bromophenyl)amino]-6,7-diethoxyquinazoline); 24, SU11652 (5-[(Z)-(5-chloro-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-N-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxamide); 27, N-(4-pyridyl)-N′-(2,4,6-trichlorophenyl) urea; 30, 4,5-dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzaldehyde; 35, SB 202190 [4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)1H-imidazole]; and 43, (5-PHENYL-2-ureido)thiophene-3-carboxamide. (B) Immunocytochemical determination for the altered expression of the MSC-specific marker CD90 and cardiac-specific markers cTnT, myosin light chain (MLC), myosin heavy chain (MHC), and Cx43 in control MSCs and the ccMSCs at the designated days after treatment. (Scale bar: 50 μm. Magnification: 400×.) (C) Immunocytochemical analysis for the homogenic characterization of the ccMSCs. Blue indicates nuclei and green is FITC for specific cardiac markers. (Magnification: 100×. Scale bar: 250 μm.) (D) Functional behavior of the ccMSCs by NE stimulus. (E) Blocking of NE-induced hypertrophic signals by prazosin. (F) Altered expression of Ca2+ homeostasis-related proteins sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA 2a) and L-type Ca2+ channel (LTCC) in MSCs and the ccMSCs. All data are expressed as means ± SEM (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).