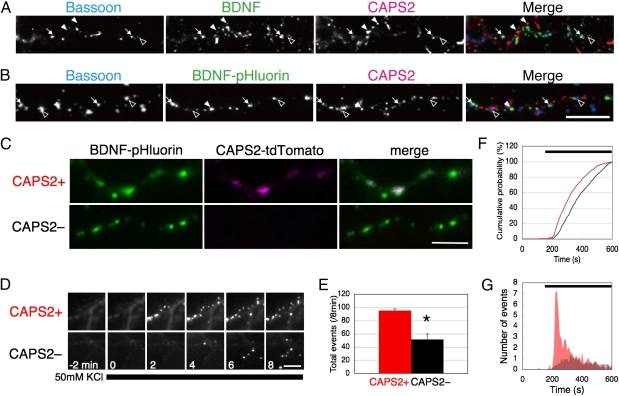
Fig. 1.
CAPS2 enhances BDNF secretion in hippocampal neurons, (A and B) Colocalization of CAPS2 and bassoon with (A) endogenous BDNF or (B) exogenously expressed BDNF-pHluorin in WT hippocampal cultures. Colocalization of BDNF (or BDNF-pHluorin) and CAPS2 in synapses (arrows) and in extrasynaptic zones (filled arrowheads) and of CAPS2 without BDNF (or BDNF-pHluorin) in synapses (open arrowheads) are indicated. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (C) Hippocampal neurons from CAPS2-KO mice were transfected with BDNF-pHluorin, with (Upper Row) or without (Lower row) CAPS2-tdTomato. (Scale bar, 2 μm.) (D) BDNF-pHluorin exocytosis events were induced by stimulation with 50 mM KCl (indicated by thick bar at bottom). Images were taken every 2 min from 2 min before until 8 min after stimulation. (Scale bar, 2 μm.) (E) Number of total events during an 8-min recording. Error bars represent SEM. *P < 0.05 using Student's t test. (F) Cumulative distribution of BDNF-pHluorin fluorescence events in the presence (red) and absence (black) of CAPS2-tdTomato. The thick bar indicates the duration of 50-mM KCl stimulation. P < 0.05 using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. (G) Histogram of events in the presence (red) and absence (gray) of CAPS2-tdTomato. (E–G) n = 12 cells from three (CAPS2+) or four (CAPS2–) different cultures per transfection.