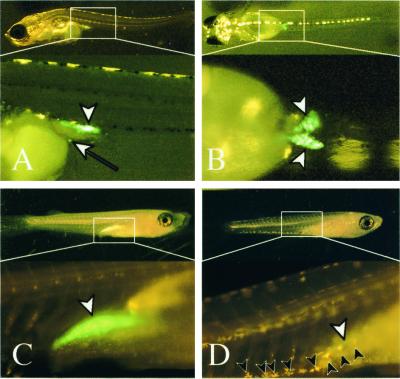
Figure 4.
GFP fluorescent germ cells after hatching. Lateral (A), dorsal (B, Upper), and ventral (B, Lower) views at day of hatching (himedaka). An ectopically located germ cell on the yolk surface cells can be observed by GFP fluorescence (white arrow in A). Female (C) and male (D) 3 weeks after hatching (Qurt E). Leucophores are seen as yellow pigments on genetic males (black arrowheads in D), whereas females (C) have no leucophores. Three weeks after hatching (C and D), sexual dimorphisms of gonads with the fluorescence within the gonads are apparent. The female gonad (white arrowhead in C, ovary) contains numerous oocytes, whereas germ cells have not proliferated well in the testis, which can be seen as a green streak (white arrowhead in D). gonad (white arrowheads).