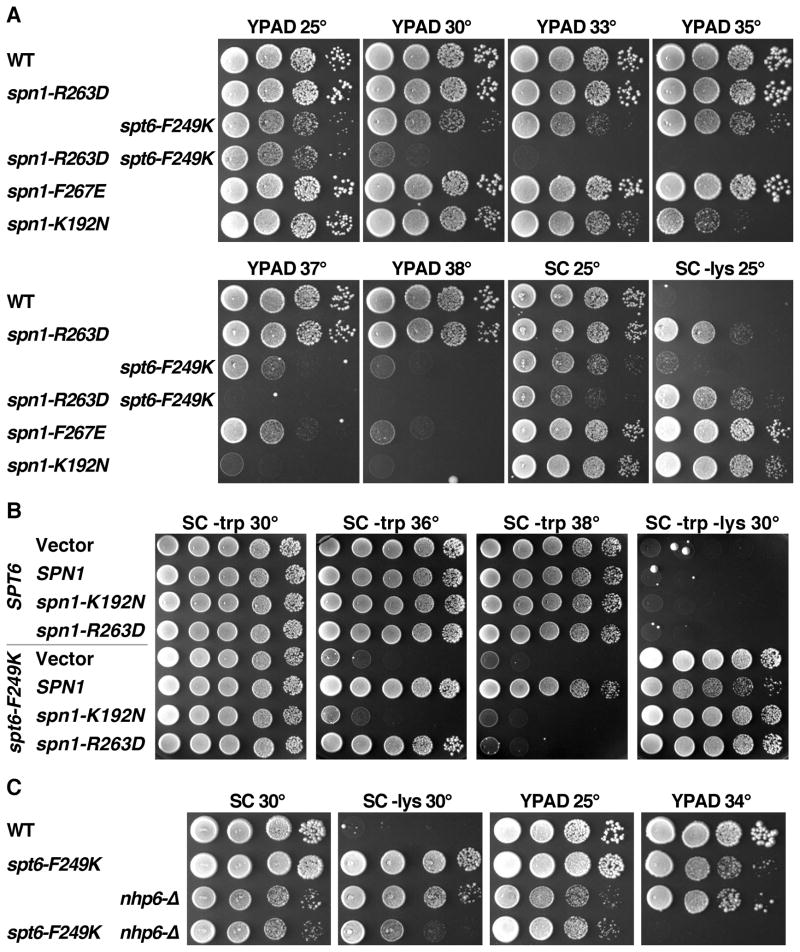
Figure 5. The Spn1-Spt6 interaction is significant for the essential activities of each protein in vivo.
(A) Isogenic strains from the A364a genetic background and with the relevant genotypes indicated (Supplemental Information) were grown to saturation in rich medium, then aliquots of 10-fold serial dilutions were placed on solid medium and incubated as labeled. SC is synthetic medium (complete or lacking tryptophan or lysine as noted) and YPAD is rich medium. Growth on medium lacking lysine reveals the Spt− phenotype, reporting here on aberrant transcription initiation from the lys2-128∂ allele. The strain with the spt6-F249K allele grows slowly on SC – lys at 25°, but the Spt− phenotype is more robust at 30° (panel B).
(B) As in panel A. nhp6-Δ indicates deletion of both NHP6A and NHP6B.
(C) WT and spt6-F249K strains were transformed with a high copy number vector, or the same vector carrying the version of SPN1 noted (Supplemental Information). Multiple transformants were tested to insure that the phenotypes detected are typical, then one clone of each was grown to saturation in synthetic medium lacking tryptophan to select for retention of the plasmids. Aliquots of 10-fold serial dilutions were placed on solid synthetic medium as in panel A and incubated as indicated.