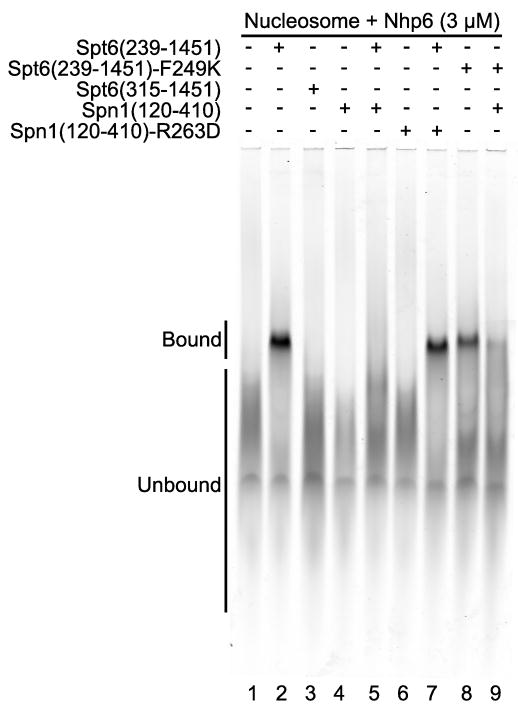
Figure 6. Spt6 binds nucleosomes and is competed by Spn1.
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay visualizing the signal from the labeled DNA incorporated into the nucleosomes (Cy5, 633 nm). All reactions included 150 fmoles of nucleosomes, 3 μM Nhp6, and 2 μM of the indicated Spt6 or Spn1 proteins. Migration positions of bound and unbound nucleosomes are indicated. Addition of Spn1 reduced the amount of Spt6-nucleosome complex from 37% of the total signal in lane 2 to 3.2% in lane 5 (9% remaining), but Spn1-R263D only reduced it to 28% (76% remaining). Spt6-F249K formed a lower amount of stable complex (18%) but Spn1 was less effective at inhibiting this (6% bound, or 36% of the original signal remaining comparing lanes 8 and 9) than it was with WT Spt6 (9% of the original signal remaining).