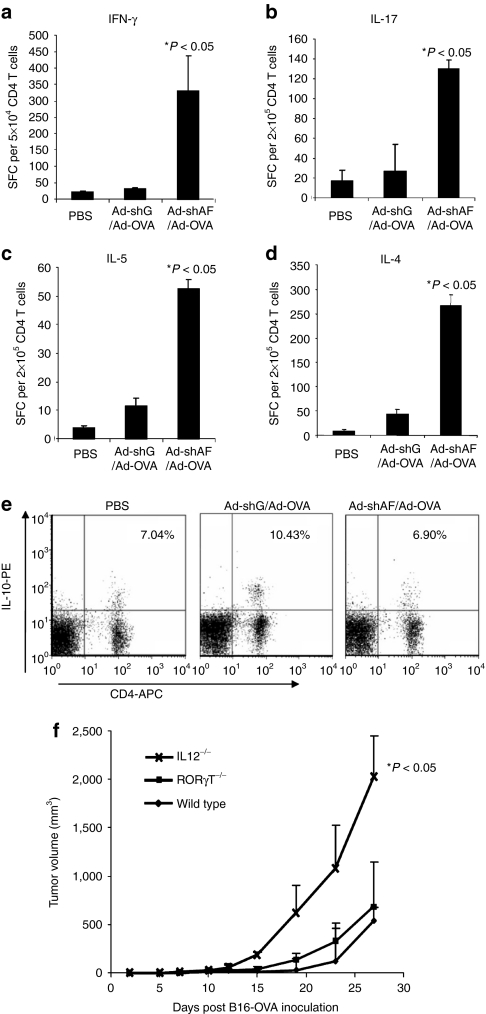
Figure 5.
Ad-shAF/Ad-OVA induces robust Th1, Th2, and Th17 responses in vivo. C57BL/6 mice were immunized intramuscularly (i.m.) with 1 × 1010 virus particles of Ad-shAF/Ad-OVA or Ad-shGFP/Ad-OVA in 50 µl sterile PBS or PBS control. Isolated CD4+ T cells from spleen were subjected to (a) IFN-γ, (b) IL-17, (c) IL-5, or (d) IL-4 ELISPOT assays. (e) Lymph node cells were prepared and subjected for IL-10 intracellular staining (Ad-shAF/Ad-OVA versus Ad-shGFP/Ad-OVA: P < 0.05). (f) Comparison of antitumor activity: wild-type C57BL/6 mice, CD4−/− mice, IL12−/− mice, or RORγT−/− mice were inoculated subcutaneously with B16-OVA tumor cells (5 × 105) and 8 days later were immunized i.m. with 1 × 1010 virus particles of Ad-shAF/Ad-OVA followed by intravenous injection of activated OT-I T cells (2 × 106) through tail vein at day 10 (P < 0.05, wild-type mice versus IL-12−/− mice). Ad-shAF, adenoviral vector coexpressing an A20-specific short-hairpin RNA and a secretory form of flagellin; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; OVA, ovalbumin; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; SFC, spot-forming cell.